Inhibitory function of parathyroid hormone-related protein on chondrocyte hypertrophy: the implication for articular cartilage repair
- PMID: 22971952
- PMCID: PMC3580589
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4025
Inhibitory function of parathyroid hormone-related protein on chondrocyte hypertrophy: the implication for articular cartilage repair
Abstract
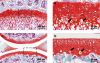
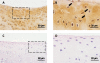
Cartilage repair tissue is usually accompanied by chondrocyte hypertrophy and osseous overgrowths, and a role for parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) in inhibiting chondrocytes from hypertrophic differentiation during the process of endochondral ossification has been demonstrated. However, application of PTHrP in cartilage repair has not been extensively considered. This review systemically summarizes for the first time the inhibitory function of PTHrP on chondrocyte hypertrophy in articular cartilage and during the process of endochondral ossification, as well as the process of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation. Based on the literature review, the strategy of using PTHrP for articular cartilage repair is suggested, which is instructive for clinical treatment of cartilage injuries as well as osteoarthritis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The promotion of osteochondral repair by combined intra-articular injection of parathyroid hormone-related protein and implantation of a bi-layer collagen-silk scaffold.Biomaterials. 2013 Aug;34(25):6046-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.04.055. Epub 2013 May 20. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 23702148
-
Human articular chondrocytes secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein and inhibit hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in coculture during chondrogenesis.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Sep;62(9):2696-706. doi: 10.1002/art.27565. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20496422
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein is induced by hypoxia and promotes expression of the differentiated phenotype of human articular chondrocytes.Clin Sci (Lond). 2013 Nov;125(10):461-70. doi: 10.1042/CS20120610. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23662774
-
The Regulatory Role of Signaling Crosstalk in Hypertrophy of MSCs and Human Articular Chondrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 14;16(8):19225-47. doi: 10.3390/ijms160819225. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26287176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule compounds promote the proliferation of chondrocytes and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in cartilage tissue engineering.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110652. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110652. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32942151 Review.
Cited by
-
The evolution of hominin bipedalism in two steps.Nature. 2025 Aug 27. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09399-9. Online ahead of print. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40866708
-
Application of kartogenin for the treatment of cartilage defects: current practice and future directions.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 21;14(45):33206-33222. doi: 10.1039/d4ra06558a. eCollection 2024 Oct 17. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39434994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supplementation of articular cartilage-derived chondroprogenitors with bone morphogenic protein-9 enhances chondrogenesis without affecting hypertrophy.Biotechnol Lett. 2022 Sep;44(9):1037-1049. doi: 10.1007/s10529-022-03280-9. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Biotechnol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35920961
-
Human pluripotent stem cell-derived chondroprogenitors for cartilage tissue engineering.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Jul;77(13):2543-2563. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03445-2. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31915836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporomandibular Joint Fibrocartilage Contains CD105 Positive Mouse Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells with Increased Chondrogenic Potential.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2023 Sep;22(3):559-570. doi: 10.1007/s12663-022-01721-6. Epub 2022 May 9. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2023. PMID: 37534349 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

