Motivational interviewing for improving outcomes in youth living with HIV
- PMID: 22972147
- PMCID: PMC11830469
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009748.pub2
Motivational interviewing for improving outcomes in youth living with HIV
Abstract
Background: Almost half of all the new HIV infections occur in youth. Motivational interviewing (MI) is a counselling technique that is effective in bringing about positive behavior changes in the general population. It is unclear whether it can be used to improve outcomes in youth living with HIV.
Objectives: To determine whether MI is effective in improving outcomes in youth living with HIV.
Search methods: We used a comprehensive and exhaustive strategy in an attempt to identify all relevant studies, regardless of language or publication status, in electronic databases (PubMed, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, EMBASE, LILACS, CINAHL, PsycINFO), conference proceedings and specialised databases from January 1980 to March 2012.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in which youth (aged 10 to 24) living with HIV received MI, singly or in combination with another intervention compared to any other intervention, and reporting on the outcomes of interest (adherence to medication, mortality, quality of life, viral load, CD4-positive-T-lymphocyte count, progression to AIDS, retention in care, substance abuse and condom use). All settings were considered.
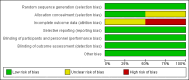
Data collection and analysis: We identified 863 references.Two authors independently examined the titles and abstracts of all identified trials, of which 28 full-text articles were closely screened for eligibility based on criteria established a-priori. The included studies were appraised for quality in duplicate. Data were extracted using a pre-tested and standardised form. No meta-analyses were performed.
Main results: Two trials located in the United States, reported in four papers met our inclusion criteria. They enrolled a total of 237 participants and compared motivational interviewing singly to standard of care. None of these trials reported on adherence to HIV medication, mortality or quality of life. Both trials reported reductions in viral load (in the short term) and unprotected sexual acts. A reduction in alcohol use was identified only in one of two studies that reported on this outcome. One trial reported on retention. Retention rates were not affected by the intervention.
Authors' conclusions: There is moderate quality evidence, coming from two trials which suggests that MI is effective in reducing short term viral load and unprotected sexual acts. There is moderate quality evidence from one trial that MI is effective in reducing alcohol use. There is a need for more trials which report on outcomes such as adherence to medication, mortality and quality of life in youth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
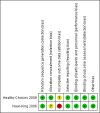
Healthy Choices 2009 {published data only}
-
- Naar‐King S, Parsons JT, Murphy DA, Chen X, Harris DR, Belzer ME. Improving health outcomes for youth living with the human immunodeficiency virus: a multisite randomized trial of a motivational intervention targeting multiple risk behaviors. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2009;163(12):1092‐8. [PUBMED: 19996045] - PMC - PubMed
Naar‐King 2006 {published data only}
-
- Naar‐King S, Wright K, Parsons JT, Frey M, Templin T, Lam P, et al. Healthy choices: motivational enhancement therapy for health risk behaviors in HIV‐positive youth. AIDS education and prevention : official publication of the International Society for AIDS Education 2006;18(1):1‐11. [PUBMED: 16539572] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Holstad 2011 {published data only}
Jacobs 2010 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs RJ, Fernandez MI, Bowen GS. Development of an internet‐based intervention using motivational interviewing culturally tailored for young Hispanic MSM. AIDS 2010 ‐ XVIII International AIDS Conference. 2010; Vol. Abstract no. WEPE0402 .
Krummenacher 2011 {published data only}
-
- Krummenacher I, Cavassini M, Bugnon O, Schneider MP. An interdisciplinary HIV‐adherence program combining motivational interviewing and electronic antiretroviral drug monitoring. AIDS care 2011;23(5):550‐61. [PUBMED: 21271406] - PubMed
Merlo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Merlo LJ, Naar‐King S, Green‐Jones M. Computer‐based motivational intervention promotes condom use among urban youth with HIV. Comprehensive psychiatry 2010;51(6):e7.
Naar‐King 2007 {published data only}
Naar‐King 2008 {published data only}
-
- Naar‐King S, Lam P, Wang B, Wright K, Parsons JT, Frey MA. Brief report: maintenance of effects of motivational enhancement therapy to improve risk behaviors and HIV‐related Health in a randomized controlled trial of youth living with HIV. Journal of pediatric psychology 2008;33(4):441‐5. [PUBMED: 17905800] - PubMed
Naar‐King 2009a {published data only}
-
- Naar‐King S, Outlaw A, Green‐Jones M, Wright K, Parsons JT. Motivational interviewing by peer outreach workers: a pilot randomized clinical trial to retain adolescents and young adults in HIV care. AIDS care 2009;21(7):868‐73. [PUBMED: 20024744] - PubMed
Naar‐King 2010 {published data only}
-
- Naar‐King S, Parsons JT, Murphy D, Kolmodin K, Harris DR. A multisite randomized trial of a motivational intervention targeting multiple risks in youth living with HIV: initial effects on motivation, self‐efficacy, and depression. The Journal of adolescent health : official publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine 2010;46(5):422‐8. [PUBMED: 20413077] - PMC - PubMed
Outlaw 2010 {published data only}
-
- Outlaw AY, Naar‐King S, Parsons JT, Green‐Jones M, Janisse H, Secord E. Using motivational interviewing in HIV field outreach with young African American men who have sex with men: a randomized clinical trial. American journal of public health 2010;100 Suppl 1:S146‐51. [PUBMED: 20147689] - PMC - PubMed
Picciano 2001 {published data only}
-
- Picciano JF, Roffman RA, Kalichman SC, Rutledge SE, Berghuis JP. A telephone based brief intervention using motivational enhancement to facilitate HIV risk reduction among MSM: A pilot study. AIDS & Behavior 2001; Vol. 5, issue 3:251‐62. [CN‐00426191]
Samet 2005 {published data only}
-
- Samet JH, Horton NJ, Meli S, Dukes K, Tripps T, Sullivan L, et al. A randomized controlled trial to enhance antiretroviral therapy adherence in patients with a history of alcohol problems. Antiviral therapy 2005;10(1):83‐93. [PUBMED: 15751766] - PubMed
Velasquez 2009 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
DiIorio 2008 {published data only}
Goggin 2010 {published data only}
-
- Goggin K, Gerkovich M, Williams K, Banderas J, Catley D, Berkley‐Patton J, Bradley‐Ewing A, Thomson N, Carruth T, Kakolewski K, Martinez D, Liston R, Pinkston‐Camp M, Clark K, Stanford J, Neville S, Kumar V, Bamberger D, Clough L. Outcomes of Project MOTIV8: A RCTof Novel Behavioral Interventions for ARTAdherence. 5th International Conference on HIV TREATMENT ADHERENCE. Journal of the International Association of Physicians in AIDS Care (JIAPAC) July;9(4):240‐67 (Abstract 62097).
Golin 2006 {published data only}
-
- Golin CE, Earp J, Tien HC, Stewart P, Porter C, Howie L. A 2‐arm, randomized, controlled trial of a motivational interviewing‐based intervention to improve adherence to antiretroviral therapy (ART) among patients failing or initiating ART. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 2006;42(1):42‐51. [PUBMED: 16763491] - PMC - PubMed
Golin 2011 {published data only}
Ingersoll 2011 {published data only}
Parsons 2007 {published data only}
-
- Parsons JT, Golub SA, Rosof E, Holder C. Motivational interviewing and cognitive‐behavioral intervention to improve HIV medication adherence among hazardous drinkers: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of acquired immune deficiency syndromes (1999) 2007;46(4):443‐50. [PUBMED: 18077833] - PMC - PubMed
van Loggerenberg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Loggerenberg F, Grant A, Naidoo K, Murrman M, GengiahS, Gengiah T, Karim SA. Group Counseling Achieves High Adherence to Antiretroviral Therapy: Resultsof the CAPRISA 058 Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Group Versus Individualized Adherence Counseling Strategies in Durban,South Africa. 5th International Conference on HIV TREATMENT ADHERENCE. Journal of the International Association of Physicians in AIDS Care (JIAPAC) July;9(4):240‐67 (Abstract 62157).
References to ongoing studies
NCT00218634 {published data only}
-
- Skills Based Counseling for Adherence and Depression in HIV+ Methadone Patients ‐ 1. Ongoing study February 2005.
NCT00794391 {published data only}
-
- Effects of Motivational Interviewing on Risky Injecting Practices Among Injecting Drug Users (IDUs). Ongoing study November 2008.
NCT01122186 {published data only}
-
- Intervention Targeting Medication Adherence and Methamphetamine Use in HIV Positive Men (ACE). Ongoing study September 2007.
NCT01347437 {published data only}
-
- Improving Antiretroviral Medication Adherence Among HIV‐infected Youth. Ongoing study July 2011.
NCT01554423 {published data only}
-
- Four‐Arm Randomized Control Trial of Brief MI Versus Couples‐Based HIV/STI Prevention in South Africa (SA R01). Ongoing study July 2010.
Additional references
CASAA 2011
-
- CASAA: Centre on Alcoholism, Substance Abuse, Addiction. Coding instruments. 2011. [http://casaa.unm.edu/codinginst.html]
Chen 2011
Cook 1995
-
- Cook Richard J, Farewell Vern T. Conditional inference for subject‐specific and marginal agreement: Two families of agreement measures. Can J Statistics 1995;23(4):333‐44.
Cooperman 2005
-
- Cooperman NA, Arnsten JH. Motivational interviewing for improving adherence to antiretroviral medications. Current HIV/AIDS reports 2005;2(4):159‐64. [PUBMED: 16343372] - PubMed
Dunn 2001
-
- Dunn C, Deroo L, Rivara FP. The use of brief interventions adapted from motivational interviewing across behavioral domains: a systematic review. Addiction (Abingdon, England) 2001;96(12):1725‐42. [PUBMED: 11784466] - PubMed
FHI 2010
-
- Family Health International. Young People Most at Risk of HIV: A Meeting Report and Discussion Paper from the Interagency Youth Working Group, U.S. Agency for International Development, the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) Inter‐Agency Task Team on HIV and Young People, and FHI. 2010. [https://www.unfpa.org/public/cache/offonce/home/publications/pubs_hiv;js...
GradePro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Bozek J, Oxman A, Schunemann O. Grade Profiler. Version 3.6 for windows. The Grade Working Group, 2008.
Guyatt 2008
Hettema 2005
-
- Hettema J, Steele J, Miller WR. Motivational interviewing. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology 2005;1:91‐111. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 2008.
Ioannidis 2007
Kiragu 2001
-
- Kiragu K. Youth and HIV/AIDS: Can we avoid catastrophe?. Population Reports 2001; Vol. 29, issue 3.
Leffingwell 2006
-
- Leffingwell T. Motivational Interviewing Knowledge and AttitudesTest (MIKAT) for Evaluation of Training Outcomes. MINT Bulletin 2006;13(1):10‐11.
Meade 2000
-
- Meade MO, Cook RJ, Guyatt GH, Groll R, Kachura JR, Bedard M, et al. Interobserver variation in interpreting chest radiographs for the diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2000;161(1):85‐90. [PUBMED: 10619802] - PubMed
Miller 1983a
-
- Miller WR. Motivational interviewing with problem drinkers. Behavioural Psychotherapy 1983;11:147‐172.
Miller 1983b
-
- Miller WR, Baca LM. Two‐year follow‐up of bibliotherapy and therapist‐directed controlled drinking training for problem drinkers. Behavior Therapy 1983;14:441‐48.
Miller 1992
-
- Miller WR, Zweben A, DiClemente CC, Rychtarik RG. Motivational enhancement therapy manual: A clinical research guide for therapists treating individuals with alcohol abuse and dependence. Project MATCH Monograph Series 1992; Vol. 2.
Miller 2008
-
- Miller WR, Moyers TB, Ernst D, Amrhein P. Manual for the Motivational Interviewing Skill Code (MISC) Version 2.1. New Mexico: Centre on Alcoholism, Substance Abuse and Addictions, The University of New Mexico 2008. [casaa.unm.edu/download/misc.pdf]
Miller 2009a
-
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. Ten things motivational interviewing is not. Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy 2009;37:129‐140. - PubMed
Miller 2009b
Miller 2010
-
- Miller WR, Rollnick S. What makes it motivational interviewing?. Plenary session of the Second International Conference on Motivational Interviewing. Stockholm, Sweden, June 7‐9, 2010. [http://www.motiverandesamtal.org/ICMI/What%20Makes%20It%20MI]
Moher 2009
Moyers 2003
-
- Moyers TB, Martin T, Manuel JK, Miller WR. The motivational interviewing treatment integrity (MITI) code. Version 3.0.. 2003. [http://casaa.unm.edu/download/miti3.pdf.]
Murphy 2012
Naar‐King 2009
-
- Naar‐King S, Parsons JT, Murphy DA, Chen X, Harris DR, Belzer ME. Improving health outcomes for youth living with the human immunodeficiency virus: a multisite randomized trial of a motivational intervention targeting multiple risk behaviors. Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine 2009;163(12):1092‐8. [PUBMED: 19996045] - PMC - PubMed
Naranbhai 2011
Pocock 1983
-
- Pocock CJ. Clinical Trials: A Practical Approach. Chichester: Wiley, 1983.
Revman 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (Revman). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Rubak 2005
Smedslund 2011
Thrasher 2006
-
- Thrasher AD, Golin CE, Earp JA, Tien H, Porter C, Howie L. Motivational interviewing to support antiretroviral therapy adherence: the role of quality counseling. Patient education and counseling 2006;62(1):64‐71. [PUBMED: 16023824] - PubMed
UNAIDS 2007
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). [AIDS Epidemic Update]. 2007. - PubMed
UNAIDS 2008
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV AIDS (UNAIDS). Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. 2008.
UNAIDS 2009
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). AIDS Epidemic Update. 2009. - PubMed
UNAIDS 2010
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. 2010.
United Nations 2010
-
- United Nations. United Nations World Youth Report: Youth and climate change. 2010. [http://social.un.org/index/WorldYouthReport.aspx]
Viera 2005
-
- Viera JA, Garrett JM. Understanding the interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Family Medicine 2005;37(5):360‐3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

