Size dependent aqueous dispersibility of carboxylated multiwall carbon nanotubes
- PMID: 22972403
- PMCID: PMC3752666
- DOI: 10.1039/c2em30405h
Size dependent aqueous dispersibility of carboxylated multiwall carbon nanotubes
Abstract
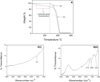
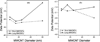
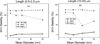
The size dependent colloidal behavior of aqueous dispersions of carboxylated multiwall carbon nanotubes (c-MWCNTs) is presented. The presence of carboxylic groups provided electrostatic stabilization in water, where the size affected agglomeration. While aspect ratio did not show any definite correlation, the hydrophobicity indices (HI), zeta potential and aggregation kinetics showed dependence on the length of the c-MWCNTs where the shorter c-MWCNTs showed significantly lower HI values, smaller particle aggregates, higher zeta potential values and higher critical coagulation concentrations (ccc) in the presence of electrolytes. Although the diameter of the short c-MWCNTs did not appear to influence their aggregation behavior, the longer c-MWCNTs showed a dependence on diameter where stability decreased with increasing CNT diameter.
Figures





References
-
- O’Connell MJ, Boul P, Ericson LM, Huffman C, Wang Y, Haroz E, Kuper C, Tour J, Ausman KD, Smalley RE. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001;342:265–271.
-
- Zorbas V, Ortiz-Acevedo A, Dalton AB, Yoshida MM, Dieckmann GR, Draper RK, Baughman RH, Jose-Yacaman M, Musselman IH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004;126:7222–7227. - PubMed
-
- Lin Y, Allard LF, Sun Y-P. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:3760–3764.
-
- Jeynes JCG, Mendoza E, Chow DCS, Watts PCP, McFadden J, Silva SRP. Adv Mater. 2006;18:1598–1602.
-
- Chen Y, Iqbal Z, Mitra S. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007;17:3946–3951.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

