Molecular typing of Treponema pallidum: a 5-year surveillance in Shanghai, China
- PMID: 22972832
- PMCID: PMC3486273
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01195-12
Molecular typing of Treponema pallidum: a 5-year surveillance in Shanghai, China
Abstract
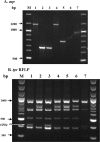
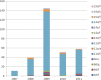
Previously, a small study showed that 14f was the predominant subtype of Treponema pallidum in Shanghai, China. The result was quite different from the genotype distribution in other areas of China. This study aimed to identify the strain types of Treponema pallidum in samples collected over a 5-year period in Shanghai. From 2007 to 2011, genital swabs were collected from patients with syphilis from the Shanghai Skin Disease Hospital. Positive specimens were typed by the enhanced typing method by adding a tp0548 gene to the existing arp and tpr genotype system. In total, 304 of the 372 enrolled patients yielded fully typeable DNA. Ten arp types (4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 19), 3 tpr types (a, d, and o), and 5 tp0548 types (a, c, f, g, and i) were identified. In total, 12 subtypes were identified with a combination of the arp and tpr genes. Subtype 14d was found in 270 samples (88.8%). When the combination included the tp0548 gene, the 12 CDC subtypes identified were divided into 14 strain types. The predominant type was 14d/f (88.8%), followed by 15d/f (3.6%), 13d/f (1.3%), and 19d/c (1.3%). Two of the 44 14d/f-infected patients and both of the 19d/c-infected patients who underwent a lumbar puncture were diagnosed with neurosyphilis. This study showed that the predominant type in Shanghai was 14d/f. While this is in keeping with data from other areas in China, it is different from an earlier report showing that 14f is the most common genotype in Shanghai. Further studies are needed to better understand the association between strain types and neurosyphilis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Molecular typing of Treponema pallidum: identification of a new sequence of tp0548 gene in Shandong, China.Sex Transm Dis. 2014 Sep;41(9):551. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000155. Sex Transm Dis. 2014. PMID: 25118968 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chinese Center for Disease Prevention and Control; Center for, STI, and AIDS Prevention and Control 2012. 2011 report on syphilis and gonorrhea epidemic analysis in China. Bull. STI Prev. Control 26:9–19
-
- Cole MJ, Chisholm SA, Palmer HM, Wallace LA, Ison CA. 2009. Molecular epidemiology of syphilis in Scotland. Sex. Transm. Infect. 85:447–451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

