An interaction between human papillomavirus 16 E2 and TopBP1 is required for optimum viral DNA replication and episomal genome establishment
- PMID: 22973044
- PMCID: PMC3497701
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01002-12
An interaction between human papillomavirus 16 E2 and TopBP1 is required for optimum viral DNA replication and episomal genome establishment
Abstract
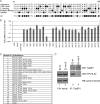
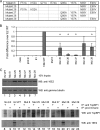
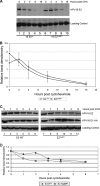
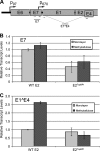
In human papillomavirus DNA replication, the viral protein E2 forms homodimers and binds to 12-bp palindromic DNA sequences surrounding the origin of DNA replication. Via a protein-protein interaction, it then recruits the viral helicase E1 to an A/T-rich origin of replication, whereupon a dihexamer forms, resulting in DNA replication initiation. In order to carry out DNA replication, the viral proteins must interact with host factors that are currently not all known. An attractive cellular candidate for regulating viral replication is TopBP1, a known interactor of the E2 protein. In mammalian DNA replication, TopBP1 loads DNA polymerases onto the replicative helicase after the G(1)-to-S transition, and this process is tightly cell cycle controlled. The direct interaction between E2 and TopBP1 would allow E2 to bypass this cell cycle control, resulting in DNA replication more than once per cell cycle, which is a requirement for the viral life cycle. We report here the generation of an HPV16 E2 mutant compromised in TopBP1 interaction in vivo and demonstrate that this mutant retains transcriptional activation and repression functions but has suboptimal DNA replication potential. Introduction of this mutant into a viral life cycle model results in the failure to establish viral episomes. The results present a potential new antiviral target, the E2-TopBP1 interaction, and increase our understanding of the viral life cycle, suggesting that the E2-TopBP1 interaction is essential.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CK2 Phosphorylation of Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 on Serine 23 Promotes Interaction with TopBP1 and Is Critical for E2 Interaction with Mitotic Chromatin and the Viral Life Cycle.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0116321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01163-21. Epub 2021 Sep 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34544280 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence supporting a role for TopBP1 and Brd4 in the initiation but not continuation of human papillomavirus 16 E1/E2-mediated DNA replication.J Virol. 2015 May;89(9):4980-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00335-15. Epub 2015 Feb 18. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25694599 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with TopBP1 Is Required for Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 Plasmid Segregation/Retention Function during Mitosis.J Virol. 2022 Aug 24;96(16):e0083022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00830-22. Epub 2022 Jul 26. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35880889 Free PMC article.
-
A new role for human papillomavirus 16 E2: Mitotic activation of the DNA damage response to promote viral genome segregation.Tumour Virus Res. 2024 Dec;18:200291. doi: 10.1016/j.tvr.2024.200291. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Tumour Virus Res. 2024. PMID: 39245413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The functions of papillomavirus E2 proteins.Virology. 2025 Feb;603:110387. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2024.110387. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Virology. 2025. PMID: 39826199 Review.
Cited by
-
CK2 Phosphorylation of Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 on Serine 23 Promotes Interaction with TopBP1 and Is Critical for E2 Interaction with Mitotic Chromatin and the Viral Life Cycle.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0116321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01163-21. Epub 2021 Sep 21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34544280 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase IIβ-binding protein 1 activates expression of E2F1 and p73 in HPV-positive cells for genome amplification upon epithelial differentiation.Oncogene. 2019 Apr;38(17):3274-3287. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0633-1. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 30631149 Free PMC article.
-
Using a Human Papillomavirus Model to Study DNA Replication and Repair of Wild Type and Damaged DNA Templates in Mammalian Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 13;21(20):7564. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207564. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33066318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Persistent Human Papillomavirus Infection.Viruses. 2017 Aug 18;9(8):229. doi: 10.3390/v9080229. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28820433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cellular DNA Helicase ChlR1 Regulates Chromatin and Nuclear Matrix Attachment of the Human Papillomavirus 16 E2 Protein and High-Copy-Number Viral Genome Establishment.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01853-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01853-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbate EA, Voitenleitner C, Botchan MR. 2006. Structure of the papillomavirus DNA-tethering complex E2:Brd4 and a peptide that ablates HPV chromosomal association. Mol. Cell 24:877–889 - PubMed
-
- Antson AA, et al. 2000. Structure of the intact transactivation domain of the human papillomavirus E2 protein. Nature 403:805–809 - PubMed
-
- Bang SW, et al. 2011. Human TopBP1 localization to the mitotic centrosome mediates mitotic progression. Exp. Cell Res. 317:994–1004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

