Intraperitoneal injection of magnetic Fe₃O₄-nanoparticle induces hepatic and renal tissue injury via oxidative stress in mice
- PMID: 22973100
- PMCID: PMC3439859
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S34349
Intraperitoneal injection of magnetic Fe₃O₄-nanoparticle induces hepatic and renal tissue injury via oxidative stress in mice
Abstract
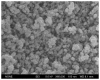
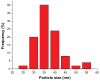
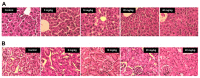
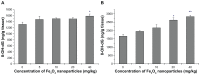
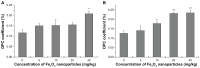
Because of its unique magnetic properties, the iron oxide (Fe₃O₄) nanoparticle has been widely exploited and its application in various fields has promised immense benefits. However, doubts exist over the use of Fe₃O₄-nanoparticles in human beings. Thus, the aim of the current study was to find out the potential safety range of medical use. Twenty-five Kunming mice were exposed to Fe₃O₄-nanoparticles via intraperitoneal injection daily for 1 week at doses of 0, 5, 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg. Hepatic and renal tissues were sliced for physiological observation. Injuries were observed in the high-dose groups (20 and 40 mg/kg) compared with the control group (0 mg/kg). Biomarkers of reactive oxygen species, glutathione, malondialdehyde, DNA-protein crosslinks, and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine in the hepatic and renal tissues were detected. Injury to tissues and oxidative damage to cells at the molecular level was found. The safest dose recommended from the results of this study is 5 mg/kg, as we believe this to be an upper limit balancing the benefits and risks for sub-long-term exposure.
Keywords: 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine; DNA-protein crosslinks; Fe3O4-nanoparticles; glutathione; malondialdehyde; reactive oxygen species.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Oxidative stress following exposure to silver and gold nanoparticles in mice.Toxicol Ind Health. 2016 Aug;32(8):1391-1404. doi: 10.1177/0748233714562623. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Toxicol Ind Health. 2016. PMID: 25548373
-
Cisplatin-induced oxidative stress stimulates renal Fas ligand shedding.Ren Fail. 2018 Nov;40(1):314-322. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2018.1456938. Ren Fail. 2018. PMID: 29619879 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of uric acid generation and blockade of glutathione dysregulation by L-arginine ameliorates dichlorvos-induced oxidative hepatorenal damage in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111443. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111443. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33667786
-
Carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic and renal damages in rat: inhibitory effects of cacao polyphenol.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(10):1669-75. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2015.1039481. Epub 2015 May 21. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25996516
-
Daily sesame oil supplementation mitigates ketoconazole-induced oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis and hepatic injury.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Nov;37:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.07.016. Epub 2016 Aug 25. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27619544
Cited by
-
Fabrication and characterization of 3D printing scaffold technology by extract oils from plant and its applications in the cardiovascular blood.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 23;11(1):24409. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03951-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34949772 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Nanoparticles in Bone Tissue Engineering.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Feb 24;12(5):757. doi: 10.3390/nano12050757. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35269245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodistribution and Clearance of Stable Superparamagnetic Maghemite Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Mice Following Intraperitoneal Administration.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 10;19(1):205. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010205. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29320407 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative DNA damage from nanoparticle exposure and its application to workers' health: a literature review.Saf Health Work. 2013 Dec;4(4):177-86. doi: 10.1016/j.shaw.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Saf Health Work. 2013. PMID: 24422173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the hepatotoxic versus the nephrotoxic role of iron oxide nanoparticles: One step forward into the dose-dependent oxidative effects.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 24;9(11):e21202. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21202. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37942152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahoo SK, Parveen S, Panda JJ. The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomedicine. 2007;3:20–31. - PubMed
-
- Kraemer SM. Iron oxide dissolution and solubility in the presence of siderophores. Aquat Sci. 2004;66:3–18.
-
- Caruthers SD, Wickline SA, Lanza GM. Nanotechnological applications in medicine. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18:26–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

