Plasmid-mediated streptomycin resistance of listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 22973158
- PMCID: PMC3433966
Plasmid-mediated streptomycin resistance of listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
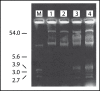
A strain of streptomycin-resistant Listeria monocytogenes LM35 isolated from imported frozen beef was examined in this study. In conjugation studies, the L. monocytogenes LM35 strain harbouring two plasmids of 54, 3.0, 2.8 and 2.7 kilobase was used as the donor and streptomycin-sensitive and plasmidless L. monocytogenes LM65 and LM100 strains as the recipients. Streptomycin resistance was transferred to L. monocytogenes LM65 and LM100 strains at frequencies of 3.3 × 10(-8) and 1.2 × 10(-9) per input donor cells, respectively. In both occasions, we also observed the concomitant transfer of the donor's 54 kilobase plasmid. These results suggest that streptomycin resistance in L. monocytogenes LM35 was mediated by the 54 kilobase plasmid.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; plasmid; streptomycin; transfer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transferable plasmid-mediated antibiotic resistance in Listeria monocytogenes.Lancet. 1990 Jun 16;335(8703):1422-6. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91447-i. Lancet. 1990. PMID: 1972210
-
Introduction of pAM beta 1 into Listeria monocytogenes by conjugation and homology between native L. monocytogenes plasmids.Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):157-61. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.157-161.1984. Infect Immun. 1984. PMID: 6323313 Free PMC article.
-
A Large-Scale Sequencing-Based Survey of Plasmids in Listeria monocytogenes Reveals Global Dissemination of Plasmids.Front Microbiol. 2021 Mar 12;12:653155. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.653155. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33776982 Free PMC article.
-
Heat Resistance Mediated by pLM58 Plasmid-Borne ClpL in Listeria monocytogenes.mSphere. 2017 Nov 1;2(6):e00364-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00364-17. eCollection 2017 Nov-Dec. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 29104933 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer of antibiotic resistance from Enterococcus faecium of fermented meat origin to Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 Apr;62(4):304-10. doi: 10.1111/lam.12553. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26854329
References
-
- Kvenberg J. E. Outbreaks of listeriosis/Listeria-contaminated foods. Microbiol. Sci. 1988;5:355–58. - PubMed
-
- Gellin BG, Broome CV. Listeriosis. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1989;261:1313–20. - PubMed
-
- Beuchat LR, Berang ME, Brackett RE. Presence and public health implications of Listeria monocytogenes on vegetable. In: Miller AL, Smith JL, Somkuti GA, editors. Foodborne listeriosis. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V. (Biomedical Division); Amsterdam: 1990. pp. 175–81.
-
- Carosella JM. Occurrence of Listeria monocytogenes in meat and poultry. In: Miller AL, Smith JL, Somkuti GA, editors. Foodborne listeriosis. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V. (Biomedical Division); Amsterdam: 1990. pp. 165–73.
-
- Marth EH, Ryser ET. Occurrence of Listeria in foods: milk and dairy foods. In: Miller AL, Smith JL, Somkuti GA, editors. Foodborne listeriosis. Elsevier Science Publishers B. V. (Biomedical Division); Amsterdam: 1990. pp. 151–64.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources