Astrocyte regulation of sleep circuits: experimental and modeling perspectives
- PMID: 22973222
- PMCID: PMC3428699
- DOI: 10.3389/fncom.2012.00065
Astrocyte regulation of sleep circuits: experimental and modeling perspectives
Abstract
Integrated within neural circuits, astrocytes have recently been shown to modulate brain rhythms thought to mediate sleep function. Experimental evidence suggests that local impact of astrocytes on single synapses translates into global modulation of neuronal networks and behavior. We discuss these findings in the context of current conceptual models of sleep generation and function, each of which have historically focused on neural mechanisms. We highlight the implications and the challenges introduced by these results from a conceptual and computational perspective. We further provide modeling directions on how these data might extend our knowledge of astrocytic properties and sleep function. Given our evolving understanding of how local cellular activities during sleep lead to functional outcomes for the brain, further mechanistic and theoretical understanding of astrocytic contribution to these dynamics will undoubtedly be of great basic and translational benefit.
Keywords: ATP; adenosine; astrocytes; computational models; glia; neuronal networks; sleep; slow oscillations.
Figures
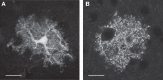

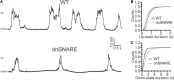
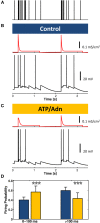
Similar articles
-
Tripartite synapses: roles for astrocytic purines in the control of synaptic physiology and behavior.Neuropharmacology. 2009 Sep;57(4):343-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.06.031. Epub 2009 Jul 3. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 19577581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Theoretical Study on the Role of Astrocytic Activity in Neuronal Hyperexcitability by a Novel Neuron-Glia Mass Model.J Math Neurosci. 2016 Dec;6(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13408-016-0042-0. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Math Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 28004309 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes: new evidence, new models, new roles.Biophys Rev. 2023 Oct 18;15(5):1303-1333. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01145-7. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 37975000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local energy on demand: Are 'spontaneous' astrocytic Ca2+-microdomains the regulatory unit for astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation?Brain Res Bull. 2018 Jan;136:54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.04.011. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 28450076 Review.
-
Physiologically-based modeling of sleep-wake regulatory networks.Math Biosci. 2014 Apr;250:54-68. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2014.01.012. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Math Biosci. 2014. PMID: 24530893 Review.
Cited by
-
NMDA-receptor antibodies alter cortical microcircuit dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 16;115(42):E9916-E9925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804846115. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30262654 Free PMC article.
-
Peeking into the sleeping brain: Using in vivo imaging in rodents to understand the relationship between sleep and cognition.J Neurosci Methods. 2019 Mar 15;316:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 9. J Neurosci Methods. 2019. PMID: 30208306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Network Models with Neuron-Astrocyte Interactions.Neuroinformatics. 2023 Apr;21(2):375-406. doi: 10.1007/s12021-023-09622-w. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Neuroinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36959372 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility and Comparability of Computational Models for Astrocyte Calcium Excitability.Front Neuroinform. 2017 Feb 21;11:11. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2017.00011. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroinform. 2017. PMID: 28270761 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes at the heart of sleep: from genes to network dynamics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 May 21;82(1):207. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05671-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40397158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bazhenov M., Timofeev I., Steriade M., Sejnowski T. (2000). Spiking-bursting activity in the thalamic reticular nucleus initiates sequences of spindle oscillations in thalamic networks. J. Neurophysiol. 84, 1076–1087 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

