Acetylation Increases EWS-FLI1 DNA Binding and Transcriptional Activity
- PMID: 22973553
- PMCID: PMC3435532
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00107
Acetylation Increases EWS-FLI1 DNA Binding and Transcriptional Activity
Abstract
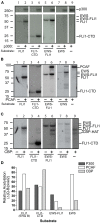
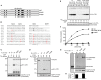
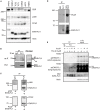
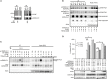
Ewing Sarcoma (ES) is associated with a balanced chromosomal translocation that in most cases leads to the expression of the oncogenic fusion protein and transcription factor EWS-FLI1. EWS-FLI1 has been shown to be crucial for ES cell survival and tumor growth. However, its regulation is still enigmatic. To date, no functionally significant post-translational modifications of EWS-FLI1 have been shown. Since ES are sensitive to histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI), and these inhibitors are advancing in clinical trials, we sought to identify if EWS-FLI1 is directly acetylated. We convincingly show acetylation of the C-terminal FLI1 (FLI1-CTD) domain, which is the DNA binding domain of EWS-FLI1. In vitro acetylation studies showed that acetylated FLI1-CTD has higher DNA binding activity than the non-acetylated protein. Over-expression of PCAF or treatment with HDI increased the transcriptional activity of EWS-FLI1, when co-expressed in Cos7 cells. However, our data that evaluates the acetylation of full-length EWS-FLI1 in ES cells remains unclear, despite creating acetylation specific antibodies to four potential acetylation sites. We conclude that EWS-FLI1 may either gain access to chromatin as a result of histone acetylation or undergo regulation by direct acetylation. These data should be considered when patients are treated with HDAC inhibitors. Further investigation of this phenomenon will reveal if this potential acetylation has an impact on tumor response.
Keywords: EWS-FLI1; Ewing’s sarcoma; PCAF; acetylation.
Figures


References
-
- Araya N., Hirota K., Shimamoto Y., Miyagishi M., Yoshida E., Ishida J., Kaneko S., Kaneko M., Nakajima T., Fukamizu A. (2003). Cooperative interaction of EWS with CREB-binding protein selectively activates hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5427–5432 10.1074/jbc.M210234200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bai Y., Srinivasan L., Perkins L., Atchison M. L. (2005). Protein acetylation regulates both PU.1 transactivation and Ig kappa 3′ enhancer activity. J. Immunol. 175, 5160–5169 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

