Dying cell clearance and its impact on the outcome of tumor radiotherapy
- PMID: 22973558
- PMCID: PMC3438527
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00116
Dying cell clearance and its impact on the outcome of tumor radiotherapy
Abstract
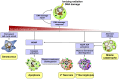
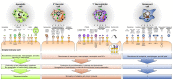
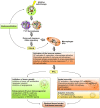
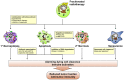
The induction of tumor cell death is one of the major goals of radiotherapy and has been considered to be the central determinant of its therapeutic outcome for a long time. However, accumulating evidence suggests that the success of radiotherapy does not only derive from direct cytotoxic effects on the tumor cells alone, but instead might also depend - at least in part - on innate as well as adaptive immune responses, which can particularly target tumor cells that survive local irradiation. The clearance of dying tumor cells by phagocytic cells of the innate immune system represents a crucial step in this scenario. Dendritic cells and macrophages, which engulf, process and present dying tumor cell material to adaptive immune cells, can trigger, skew, or inhibit adaptive immune responses, respectively. In this review we summarize the current knowledge of different forms of cell death induced by ionizing radiation, the multi-step process of dying cell clearance, and its immunological consequences with special regard toward the potential exploitation of these mechanisms for the improvement of tumor radiotherapy.
Keywords: Radiotherapy; apoptosis; dying cell clearance; mitotic catastrophe; necroptosis; necrosis; senescence.
Figures


References
-
- Afshar G., Jelluma N., Yang X., Basila D., Arvold N. D., Karlsson A., Yount G. L., Dansen T. B., Koller E., Haas-Kogan D. A. (2006). Radiation-induced caspase-8 mediates p53-independent apoptosis in glioma cells. Cancer Res. 66 4223–4232 - PubMed
-
- Ahrens S., Zelenay S., Sancho D., Hanc P., Kjaer S., Feest C., Fletcher G., Durkin C., Postigo A., Skehel M., Batista F., Thompson B., Way M., Reis E Sousa C., Schulz O. (2012). F-actin is an evolutionarily conserved damage-associated molecular pattern recognized by DNGR-1, a receptor for dead cells. Immunity 36 635–645 - PubMed
-
- Anderson H. A., Maylock C. A., Williams J. A., Paweletz C. P., Shu H., Shacter E. (2003). Serum-derived protein S binds to phosphatidylserine and stimulates the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Nat. Immunol. 4 87–91 - PubMed
-
- Apetoh L., Ghiringhelli F., Tesniere A., Criollo A., Ortiz C., Lidereau R., Mariette C., Chaput N., Mira J. P., Delaloge S., Andre F., Tursz T., Kroemer G., Zitvogel L. (2007). The interaction between HMGB1 and TLR4 dictates the outcome of anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 220 47–59 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

