Hepatoprotective effect of Bathysa cuspidata in a murine model of severe toxic liver injury
- PMID: 22974218
- PMCID: PMC3444993
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2012.00835.x
Hepatoprotective effect of Bathysa cuspidata in a murine model of severe toxic liver injury
Abstract
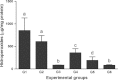
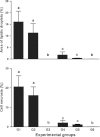
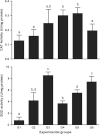
The objective of this study was to investigate the hepatoprotective effect of a bark extract of Bathysa cuspidata extract (BCE) in a murine model of severe liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl(4) ). Forty-two Wistar rats were randomized into six groups of seven animals each: Group 1(G1): CCl(4) ; Group 2 (G2): dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) + CCl(4) ; Group 3 (G3): BCE 400 mg/kg alone; Group 4 (G4): BCE 200 mg/kg + CCl(4) ; Group 5 (G5): BCE 400 mg/kg + CCl(4) ; Group 6 (G6): DMSO alone. The extract was administered by gavage for 18 days beginning 6 days prior to the first application of CCl(4) . After completing CCl(4) administration, the animals were euthanized. The animals in G1, G2, G4 and G5 experienced significant body weight loss and had an increased liver somatic index compared with G3 and G6 (P < 0.05). A significant reduction in serum aspartate and alanine transaminase and gamma-glutamyl transferase (P < 0.05) and a significant increase in the activity of the anti-oxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase were found in G5 (P < 0.05). Lower proportions of cellular necrosis and lipid droplets were found in the livers of animals in G4 and G5 compared with G1 and G2 (P < 0.05). These results confirm the marked hepatoprotective activity of the bark extract of Bathysa cuspidata in severe injuries induced by CCl(4) in rats and suggest that this effect may be associated with the inhibition of oxidative damage.
© 2012 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2012 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of bark extract of Bathysa cuspidata on hepatic oxidative damage and blood glucose kinetics in rats exposed to paraquat.Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40(1):62-70. doi: 10.1177/0192623311425059. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Toxicol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22021167
-
Hepatoprotective effect of shidagonglao on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride.Am J Chin Med. 2009;37(6):1085-97. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X0900751X. Am J Chin Med. 2009. PMID: 19938218
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Scoparia dulcis on carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury in mice.Am J Chin Med. 2010;38(4):761-75. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X10008226. Am J Chin Med. 2010. PMID: 20626061
-
Protective activity of the stem bark aqueous extract of Musanga cecropioides in carbon tetrachloride- and acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2009 Mar 7;6(2):131-8. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2009. PMID: 20209004 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of Ficus racemosa stem bark against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in albino rats.Pharm Biol. 2010 Feb;48(2):210-6. doi: 10.3109/13880200903081788. Pharm Biol. 2010. PMID: 20645843
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Anacardium occidentale L. and Anacardium microcarpum D. Extracts on the Liver of IL-10 Knockout Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Dec 7;2020:3054521. doi: 10.1155/2020/3054521. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33376496 Free PMC article.
-
Euterpe edulis Extract but Not Oil Enhances Antioxidant Defenses and Protects against Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by a High-Fat Diet in Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:8173876. doi: 10.1155/2016/8173876. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27418954 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of plants from the Brazilian Atlantic Forest led to the identification of Athenaea velutina (Solanaceae) as a novel source of antimetastatic agents.Int J Exp Pathol. 2020 Jun;101(3-4):106-121. doi: 10.1111/iep.12351. Epub 2020 May 26. Int J Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32452573 Free PMC article.
-
Trypanosoma cruzi infection and benznidazole therapy independently stimulate oxidative status and structural pathological remodeling of the liver tissue in mice.Parasitol Res. 2015 Aug;114(8):2873-81. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4488-x. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 25912691
-
Ointment of Brassica oleracea var. capitata Matures the Extracellular Matrix in Skin Wounds of Wistar Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:919342. doi: 10.1155/2015/919342. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26170889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Hameed ESS. Total phenolic contents and free radical scavenging activity of certain Egyptian Ficus species leaf samples. Food Chem. 2009;114:1271–1277.
-
- Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–126. - PubMed
-
- Bedda S, Laurent A, Conti F, et al. Mangafodipir prevents liver injury induced by acetaminophen in the mouse. J. Hepatol. 2003;39:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MA. Rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976;82:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brattin WJ, Glende EA, Jr, Recknagel RO. Pathological mechanisms in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity. J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1985;1:27–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

