Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce systemic inflammation and attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats
- PMID: 22974286
- PMCID: PMC3502090
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-9-33
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce systemic inflammation and attenuate LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats
Abstract
Background: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) possess potent immunomodulatory properties and simultaneously lack the ability to illicit immune responses. Hence, MSCs have emerged as a promising candidate for cellular therapeutics for inflammatory diseases. Within the context of this study, we investigated whether human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) could ameliorate lipopolysaccharide- (LPS-) induced acute lung injury (ALI) in a rat model.
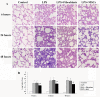
Methods: ALI was induced via injection of LPS. Rats were divided into three groups: (1) saline group(control), (2) LPS group, and (3) MSC + LPS group. The rats were sacrificed at 6, 24, and 48 hours after injection. Serum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and lungs were collected for cytokine concentration measurements, assessment of lung injury, and histology.
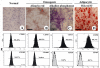
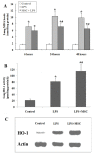
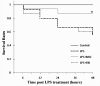
Results: UC-MSCs increased survival rate and suppressed LPS-induced increase of serum concentrations of pro-inflammatory mediators TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 without decreasing the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. The MSC + LPS group exhibited significant improvements in lung inflammation, injury, edema, lung wet/dry ratio, protein concentration, and neutrophil counts in the BALF, as well as improved myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in the lung tissue. Furthermore, UC-MSCs decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) production and increased Heme Oxygenase-1 (HO-1) protein production and activity in the lung tissue.
Conclusion: UC-MSCs noticeably increased the survival rate of rats suffering from LPS-induced lung injury and significantly reduced systemic and pulmonary inflammation. Promoting anti-inflammatory homeostasis and reducing oxidative stress might be the therapeutic basis of UC-MSCs.
Figures
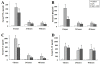
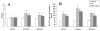
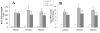
References
-
- Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, Lee JW, Serikov V, Matthay MA. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stemcells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179:1855–1863. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

