Reduced expression of α-synuclein in alcoholic brain: influence of SNCA-Rep1 genotype
- PMID: 22974310
- PMCID: PMC3543514
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00495.x
Reduced expression of α-synuclein in alcoholic brain: influence of SNCA-Rep1 genotype
Abstract
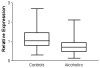
α-Synuclein has recently been implicated in the pathophysiology of alcohol abuse due to its role in dopaminergic neurotransmission. In these studies, genetic variability in the α-synuclein gene influences its expression which may contribute to susceptibility to chronic alcohol abuse. Real-time PCR was used to quantify α-synuclein mRNA expression in autopsy samples of human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Because of the association between length of the α-synuclein-repeat 1 microsatellite marker and expression levels of the gene, this marker was genotyped in a Caucasian sample of 126 controls and 117 alcoholics using capillary gel electrophoresis. The allele and genotype frequencies of α-synuclein-repeat 1 marker differed significantly between alcoholics and controls. Alcoholics had greater frequencies of the shortest allele found (267 bp). The shortest allele of the α-synuclein-repeat 1 marker was associated with decreased expression of α-synuclein in prefrontal cortex. Individuals with at least one copy of the 267 bp allele were more likely to exhibit an alcohol abuse phenotype. These results suggest that individuals with the 267 bp allele may be at increased risk of developing alcoholism and that genetic variation at the α-synuclein-repeat 1 locus may influence α-synuclein expression in the prefrontal cortex.
Keywords: Human; SNCA-Rep1; mRNA; post-mortem; prefrontal cortex.
© 2012 The Authors, Addiction Biology © 2012 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential expression of α-synuclein splice variants in the brain of alcohol misusers: Influence of genotype.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015 Oct 1;155:284-92. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.05.045. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015. PMID: 26297298
-
Alpha-synuclein, alcohol use disorders, and Parkinson disease: a case-control study.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009 Jul;15(6):430-4. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.11.011. Epub 2009 Feb 4. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2009. PMID: 19196539 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regulation of alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in various human brain tissues.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 16;4(10):e7480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007480. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19834617 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage disequilibrium and association analysis of alpha-synuclein and alcohol and drug dependence in two American Indian populations.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007 Apr;31(4):546-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2007.00338.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007. PMID: 17374033
-
The role of α-synuclein in the pathophysiology of alcoholism.Neurochem Int. 2013 Sep;63(3):154-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23791711 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-Synuclein in Alcohol Use Disorder, Connections with Parkinson's Disease and Potential Therapeutic Role of 5' Untranslated Region-Directed Small Molecules.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 21;10(10):1465. doi: 10.3390/biom10101465. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33096655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex differences in GABAA receptor subunit transcript expression are mediated by genotype in subjects with alcohol-related cirrhosis of the liver.Genes Brain Behav. 2022 Apr;21(4):e12785. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12785. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Genes Brain Behav. 2022. PMID: 35301805 Free PMC article.
-
Using autopsy brain tissue to study alcohol-related brain damage in the genomic age.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014 Jan;38(1):1-8. doi: 10.1111/acer.12243. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014. PMID: 24033426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro aggregation assays for the characterization of α-synuclein prion-like properties.Prion. 2014 Jan-Feb;8(1):19-32. doi: 10.4161/pri.28125. Prion. 2014. PMID: 24552879 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Dopamine Transporter Gene with Heroin Dependence in an Indian Subpopulation from Manipur.J Mol Neurosci. 2021 Jan;71(1):122-136. doi: 10.1007/s12031-020-01633-5. Epub 2020 Jun 18. J Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32557146
References
-
- AIHW. Australia’s health 2008. Canberra: 2008.
-
- Bonsch D, Lederer T, Reulbach U, Hothorn T, Kornhuber J, Bleich S. Joint analysis of the NACP-REP1 marker within the alpha synuclein gene concludes association with alcohol dependence. Hum Mol Genet. 2005a;14:967–971. - PubMed
-
- Bonsch D, Lederer T, Reulbach U, Hothorn T, Kornhuber J, Bleich S. Joint analysis of the NACP-REP1 marker within the α synuclein gene concludes association with alcohol dependence. Human Molecular Genetics. 2005b;14:967–971. - PubMed
-
- Buckley ST, Dodd PR. GABAA receptor ® subunit mRNA expression in the human alcoholic brain. Neurochemistry International. 2004;45:1011–1020. - PubMed
-
- Buckley ST, Foley PF, Innes DJ, Loh E-W, Shen Y, Williams SM, Harper CG, Tannenberg AEG, Dodd PR. GABAA receptor ® isoform protein expression in human alcoholic brain: interaction with genotype. Neurochemistry International. 2006;49:557–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

