Eps homology domain endosomal transport proteins differentially localize to the neuromuscular junction
- PMID: 22974368
- PMCID: PMC3541266
- DOI: 10.1186/2044-5040-2-19
Eps homology domain endosomal transport proteins differentially localize to the neuromuscular junction
Abstract
Background: Recycling of endosomes is important for trafficking and maintenance of proteins at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). We have previously shown high expression of the endocytic recycling regulator Eps15 homology domain-containing (EHD)1 proteinin the Torpedo californica electric organ, a model tissue for investigating a cholinergic synapse. In this study, we investigated the localization of EHD1 and its paralogs EHD2, EHD3, and EHD4 in mouse skeletal muscle, and assessed the morphological changes in EHD1-/- NMJs.
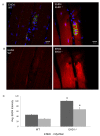
Methods: Localization of the candidate NMJ protein EHD1 was assessed by confocal microscopy analysis of whole-mount mouse skeletal muscle fibers after direct gene transfer and immunolabeling. The potential function of EHD1 was assessed by specific force measurement and α-bungarotoxin-based endplate morphology mapping in EHD1-/- mouse skeletal muscle.
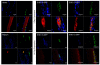
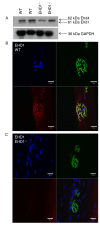
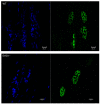
Results: Endogenous EHD1 localized to primary synaptic clefts of murine NMJ, and this localization was confirmed by expression of recombinant green fluorescent protein labeled-EHD1 in murine skeletal muscle in vivo. EHD1-/- mouse skeletal muscle had normal histology and NMJ morphology, and normal specific force generation during muscle contraction. The EHD 1-4 proteins showed differential localization in skeletal muscle: EHD2 to muscle vasculature, EHD3 to perisynaptic regions, and EHD4 to perinuclear regions and to primary synaptic clefts, but at lower levels than EHD1. Additionally, specific antibodies raised against mammalian EHD1-4 recognized proteins of the expected mass in the T. californica electric organ. Finally, we found that EHD4 expression was more abundant in EHD1-/- mouse skeletal muscle than in wild-type skeletal muscle.
Conclusion: EHD1 and EHD4 localize to the primary synaptic clefts of the NMJ. Lack of obvious defects in NMJ structure and muscle function in EHD1-/- muscle may be due to functional compensation by other EHD paralogs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential requirements for the Eps15 homology domain proteins EHD4 and EHD2 in the regulation of mammalian ciliogenesis.Traffic. 2022 Jul;23(7):360-373. doi: 10.1111/tra.12845. Epub 2022 May 17. Traffic. 2022. PMID: 35510564 Free PMC article.
-
Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 4 (EHD4) is required for Eps15 Homology Domain Protein 1 (EHD1)-mediated endosomal recruitment and fission.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 23;15(9):e0239657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239657. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32966336 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of EHD1/EHD4 protein levels interfere with L1/NgCAM endocytosis in neurons and disrupt axonal targeting.J Neurosci. 2010 May 12;30(19):6646-57. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5428-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20463227 Free PMC article.
-
The TOR Pathway at the Neuromuscular Junction: More Than a Metabolic Player?Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Aug 28;13:162. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00162. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32982690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuromuscular synapse electrophysiology in myasthenia gravis animal models.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018 Jan;1412(1):146-153. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13507. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018. PMID: 29068559 Review.
Cited by
-
EHD1 mediates vesicle trafficking required for normal muscle growth and transverse tubule development.Dev Biol. 2014 Mar 15;387(2):179-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24440153 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure and functional analysis of human C1ORF123.PeerJ. 2018 Sep 28;6:e5377. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5377. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 30280012 Free PMC article.
-
Scratching the surface: actin' and other roles for the C-terminal Eps15 homology domain protein, EHD2.Histol Histopathol. 2014 Mar;29(3):285-92. doi: 10.14670/HH-29.285. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Histol Histopathol. 2014. PMID: 24347515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eps 15 Homology Domain (EHD)-1 Remodels Transverse Tubules in Skeletal Muscle.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 1;10(9):e0136679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136679. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26325203 Free PMC article.
-
The endocytic recycling regulatory protein EHD1 Is required for ocular lens development.Dev Biol. 2015 Dec 1;408(1):41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26455409 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

