In vivo, cardiac-specific knockdown of a target protein, malic enzyme-1, in rat via adenoviral delivery of DNA for non-native miRNA
- PMID: 22974418
- PMCID: PMC3651674
- DOI: 10.2174/156652312803519760
In vivo, cardiac-specific knockdown of a target protein, malic enzyme-1, in rat via adenoviral delivery of DNA for non-native miRNA
Abstract
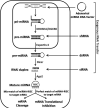
This study examines the feasibility of using the adenoviral delivery of DNA for a non-native microRNA to suppress expression of a target protein (cytosolic NADP(+)-dependent malic-enzyme 1, ME1) in whole heart in vivo, via an isolated-heart coronary perfusion approach. Complementary DNA constructs for ME1 microRNA were inserted into adenoviral vectors. Viral gene transfer to neonatal rat cardiomyocytes yielded 65% suppression of ME1 protein. This viral package was delivered to rat hearts in vivo (Adv.miR_ME1, 10(13) vp/ml PBS) via coronary perfusion, using a cardiac-specific isolation technique. ME1 mRNA was reduced by 73% at 2-6 days post-surgery in heart receiving the Adv.miR_ME1. Importantly, ME1 protein was reduced by 66% (p < 0.0002) at 5-6 days relative to sham-operated control hearts. Non-target protein expression for GAPDH, calsequestrin, and mitochondrial malic enzyme, ME3, were all unchanged. The non-target isoform, ME2, was unchanged at 2-5 days and reduced at day 6. This new approach demonstrates for the first time significant and acute silencing of target RNA translation and protein content in whole heart, in vivo, via non-native microRNA expression.
Figures





References
-
- Gray SJ, Samulski RJ. Optimizing gene delivery vectors for the treatment of heart disease. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008;8(7):911–22. - PubMed
-
- Muller OJ, Katus HA, Bekeredjian R. Targeting the heart with gene therapy-optimized gene delivery methods. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;73(3):453–62. - PubMed
-
- Poller W, Fechner H. Development of novel cardiovascular therapeutics from small regulatory RNA molecules—an outline of key requirements. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(20):2252–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

