Intracranial hemorrhage
- PMID: 22974648
- PMCID: PMC3443867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.emc.2012.06.003
Intracranial hemorrhage
Abstract
Intracranial hemorrhage refers to any bleeding within the intracranial vault, including the brain parenchyma and surrounding meningeal spaces. This article focuses on the acute diagnosis and management of primary nontraumatic intracerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage in the emergency department.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
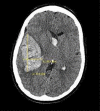
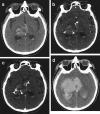
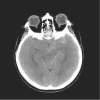
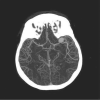
References
-
- van Asch CJJ, et al. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Neurology. 2010;9(2):167–176. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar MI, Freeman WD. Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Semin Neurol. 2010;30(5):555–64. - PubMed
-
- Broderick J, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adults. Stroke. 2007;38(6):2001–2023. - PubMed
-
- Elliott J, Smith M. The Acute Management of Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Clinical Review. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2010;110(5):1419–1427. - PubMed
-
- Feigin VL, et al. Worldwide stroke incidence and early case fatality reported in 56 population-based studies: a systematic review. The Lancet Neurology. 2009;8(4):355–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

