Reverse-mode Na+/Ca2+ exchange is an important mediator of venous contraction
- PMID: 22974823
- PMCID: PMC3502721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.08.004
Reverse-mode Na+/Ca2+ exchange is an important mediator of venous contraction
Abstract
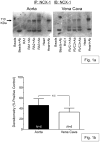
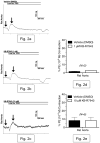
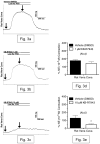
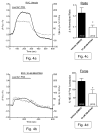
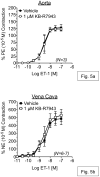
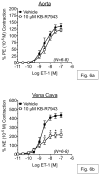
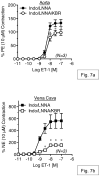
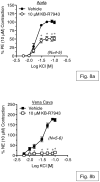
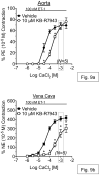
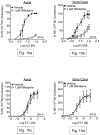
The Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger (NCX) is a bi-directional regulator of cytosolic Ca(2+), causing Ca(2+) efflux in forward-mode and Ca(2+) influx in reverse-mode. We hypothesized that reverse-mode NCX is a means of Ca(2+) entry in rat aorta (RA) and vena cava (RVC). NCX protein in RA and RVC was confirmed by immunoprecipitation. To assess NCX function, isometric contraction and intracellular Ca(2+) was measured in RA and RVC rings in response to low extracellular Na(+), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and KCl, in the presence or absence of the NCX antagonist KB-R7943. In RVC, low extracellular Na(+) caused vasoconstriction and an increase in intracellular Ca(2+) that was attenuated by 10μM KB-R7943. KB-R7943 (10 μM) attenuated maximal contraction to ET-1 in RVC (53 ± 9% of control), but not RA (91±1% of control). KB-R7943 (10 μM) reduced the maximal contraction to KCl in RA (48 ± 5%) and nearly abolished it in RVC (9 ± 2%), suggesting that voltage-dependent Ca(2+) influx may be inhibited by KB-R7943 as well. However, the L-type Ca(2+) channel inhibitor nifedipine (1 μM) did not alter ET-1-induced contraction. Our findings suggest that reverse-mode NCX is an important mechanism of Ca(2+) influx in RVC but not RA, especially during ET-1-induced contraction. Also, the effects of KB-R7943 on ET-1-induced contraction of RA and RVC are predominantly mediated by reverse-mode NCX inhibition and not due to off-target inhibition of Ca(2+) channels.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reverse-mode NCX current in mouse airway smooth muscle: Na(+) and voltage dependence, contributions to Ca(2+) influx and contraction, and altered expression in a model of allergen-induced hyperresponsiveness.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012 Jun;205(2):279-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02401.x. Epub 2012 Feb 11. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2012. PMID: 22212361
-
KB-R7943 reveals possible involvement of Na(+)-Ca2+ exchanger in elevation of intracellular Ca2+ in rat carotid arterial myocytes.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2004 Feb;40(1):35-42. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.40.35. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2004. PMID: 15170076
-
PPADS, a P2X receptor antagonist, as a novel inhibitor of the reverse mode of the Na⁺/Ca²⁺ exchanger in guinea pig airway smooth muscle.Eur J Pharmacol. 2012 Jan 15;674(2-3):439-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.11.018. Epub 2011 Nov 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22119380
-
Topics on the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: pharmacological characterization of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibitors.J Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Sep;102(1):7-16. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fmj06002x2. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 16990699 Review.
-
The role of the Na+/Ca2+-exchanger (NCX) in cancer-associated fibroblasts.Biol Chem. 2023 Jan 4;404(4):325-337. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2022-0253. Print 2023 Mar 28. Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36594183 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of forward and reverse transport of Ca2+ via Na+/Ca2+ exchangers (NCX) prevents sperm capacitation.Biol Res. 2024 Aug 23;57(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00535-9. Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 39175101 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-calcium exchanger 1 is the key molecule for urinary potassium excretion against acute hyperkalemia.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 30;15(6):e0235360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235360. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32603346 Free PMC article.
-
The Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Mitochondrial Metabolism in Cardiovascular Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 9;14(12):2760. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122760. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conditional knockout of smooth muscle sodium calcium exchanger type-1 lowers blood pressure and attenuates Angiotensin II-salt hypertension.Physiol Rep. 2015 Jan 27;3(1):e12273. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12273. Print 2015 Jan 1. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25626872 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse mode of sodium/calcium exchanger subtype 1 contributes to detrusor overactivity in rats with partial bladder outflow obstruction.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Mar 15;10(3):806-815. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29636870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Philipson KD, Nicoll DA, Ottolia M, Quednau BD, Reuter H, John S, Qiu Z. The Na+/Ca2+ exchange molecule: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;976:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Annunziato L, Pignataro G, Di Renzo GF. Pharmacology of brain Na+/Ca2+ exchanger: from molecular biology to therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:633–54. - PubMed
-
- Iwamoto T, Pan Y, Wakabayashi S, Imagawa T, Yamanaka HI, Shigekawa M. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cardiac Na+/Ca2+ exchanger via protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13609–15. - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ. Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:763–854. - PubMed
-
- Blaustein MP. Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: a reassessment and a hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1977;232:C165–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

