Mig6 is a sensor of EGF receptor inactivation that directly activates c-Abl to induce apoptosis during epithelial homeostasis
- PMID: 22975324
- PMCID: PMC3657149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.08.001
Mig6 is a sensor of EGF receptor inactivation that directly activates c-Abl to induce apoptosis during epithelial homeostasis
Abstract
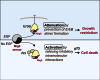
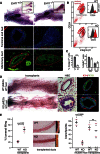
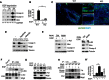
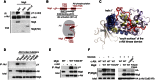
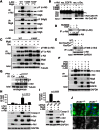
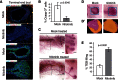
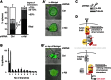
A fundamental aspect of epithelial homeostasis is the dependence on specific growth factors for cell survival, yet the underlying mechanisms remain obscure. We found an "inverse" mode of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling that directly links ErbB receptor inactivation to the induction of apoptosis. Upon ligand deprivation Mig6 dissociates from the ErbB receptor and binds to and activates the tyrosine kinase c-Abl to trigger p73-dependent apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells. Deletion of Errfi1 (encoding Mig6) and inhibition or RNAi silencing of c-Abl causes impaired apoptosis and luminal filling of mammary ducts. Mig6 activates c-Abl by binding to the kinase domain, which is prevented in the presence of epidermal growth factor (EGF) by Src family kinase-mediated phosphorylation on c-Abl-Tyr488. These results reveal a receptor-proximal switch mechanism by which Mig6 actively senses EGF deprivation to directly activate proapoptotic c-Abl. Our findings challenge the common belief that deprivation of growth factors induces apoptosis passively by lack of mitogenic signaling.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Agami R., Blandino G., Oren M., Shaul Y. Interaction of c-Abl and p73alpha and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature. 1999;399:809–813. - PubMed
-
- Amatschek S., Koenig U., Auer H., Steinlein P., Pacher M., Gruenfelder A., Dekan G., Vogl S., Kubista E., Heider K.H. Tissue-wide expression profiling using cDNA subtraction and microarrays to identify tumor-specific genes. Cancer Res. 2004;64:844–856. - PubMed
-
- Avraham R., Yarden Y. Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011;12:104–117. - PubMed
-
- Bredesen D.E., Mehlen P., Rabizadeh S. Apoptosis and dependence receptors: a molecular basis for cellular addiction. Physiol. Rev. 2004;84:411–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

