Alcohol dependence as a chronic pain disorder
- PMID: 22975446
- PMCID: PMC3612891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.07.010
Alcohol dependence as a chronic pain disorder
Abstract
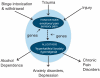
Dysregulation of pain neurocircuitry and neurochemistry has been increasingly recognized as playing a critical role in a diverse spectrum of diseases including migraine, fibromyalgia, depression, and PTSD. Evidence presented here supports the hypothesis that alcohol dependence is among the pathologies arising from aberrant neurobiological substrates of pain. In this review, we explore the possible influence of alcohol analgesia and hyperalgesia in promoting alcohol misuse and dependence. We examine evidence that neuroanatomical sites involved in the negative emotional states of alcohol dependence also play an important role in pain transmission and may be functionally altered under chronic pain conditions. We also consider possible genetic links between pain transmission and alcohol dependence. We propose an allostatic load model in which episodes of alcohol intoxication and withdrawal, traumatic stressors, and injury are each capable of dysregulating an overlapping set of neural substrates to engender sensory and affective pain states that are integral to alcohol dependence and comorbid conditions such as anxiety, depression, and chronic pain.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Angst MS, Clark JD. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: a qualitative systematic review. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:570–587. - PubMed
-
- Aharon I, Becerra L, Chabris CF, Borsook D. Noxious heat induces fMRI activation in two anatomically distinct clusters within the nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience Letters. 2006;392:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Bardin L, Malfetes N, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortère R. Chronic restraint stress induces mechanical and cold allodynia, and enhances inflammatory pain in rat: relevance to human stress-associated painful pathologies. Behavioural Brain Research. 2009;205:360–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 AA999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA008459/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AA018250/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA020608/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA007456/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AA020839/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA008459/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020608/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA012602/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AA007456/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA012602/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA008459/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- AA018250/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AA020839/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA006420/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

