Macrophages require Skap2 and Sirpα for integrin-stimulated cytoskeletal rearrangement
- PMID: 22976304
- PMCID: PMC3561861
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.111260
Macrophages require Skap2 and Sirpα for integrin-stimulated cytoskeletal rearrangement
Abstract
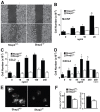
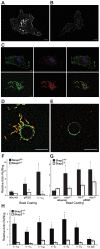
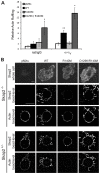
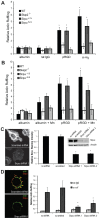
Macrophages migrate to sites of insult during normal inflammatory responses. Integrins guide such migration, but the transmission of signals from integrins into the requisite cytoskeletal changes is poorly understood. We have discovered that the hematopoietic adaptor protein Skap2 is necessary for macrophage migration, chemotaxis, global actin reorganization and local actin reorganization upon integrin engagement. Binding of phosphatidylinositol [3,4,5]-triphosphate to the Skap2 pleckstrin-homology (PH) domain, which relieves its conformational auto-inhibition, is critical for this integrin-driven cytoskeletal response. Skap2 enables integrin-induced tyrosyl phosphorylation of Src-family kinases (SFKs), Adap, and Sirpα, establishing their roles as signaling partners in this process. Furthermore, macrophages lacking functional Sirpα unexpectedly have impaired local integrin-induced responses identical to those of Skap2(-/-) macrophages, and Skap2 requires Sirpα for its recruitment to engaged integrins and for coordinating downstream actin rearrangement. By revealing the positive-regulatory role of Sirpα in a Skap2-mediated mechanism connecting integrin engagement with cytoskeletal rearrangement, these data demonstrate that Sirpα is not exclusively immunoinhibitory, and illuminate previously unexplained observations implicating Skap2 and Sirpα in mouse models of inflammatory disease.
Figures



References
-
- Adams S., van der Laan L. J., Vernon–Wilson E., Renardel de Lavalette C., Döpp E. A., Dijkstra C. D., Simmons D. L., van den Berg T. K. (1998). Signal-regulatory protein is selectively expressed by myeloid and neuronal cells. J. Immunol. 161, 1853–1859 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31 GM78720/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068150/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI065495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL032854/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM041890/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM041890/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA049152/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL07604-24/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56AI085131/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA49132/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 GM078720/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI085131/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM041890/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116327/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007604/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114945/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

