Role of ornithine decarboxylase in regulation of estrogen receptor alpha expression and growth in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 22976807
- PMCID: PMC3715085
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-012-2235-x
Role of ornithine decarboxylase in regulation of estrogen receptor alpha expression and growth in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
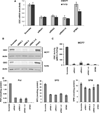
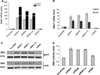
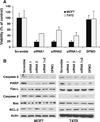
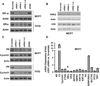
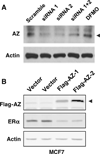
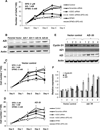
Our previous studies demonstrated that specific polyamine analogues, oligoamines, down-regulated the activity of a key polyamine biosynthesis enzyme, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), and suppressed expression of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) in human breast cancer cells. However, the mechanism underlying the potential regulation of ERα expression by polyamine metabolism has not been explored. Here, we demonstrated that RNAi-mediated knockdown of ODC (ODC KD) down-regulated the polyamine pool, and hindered growth in ERα-positive MCF7 and T47D and ERα-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. ODC KD significantly induced the expression and activity of the key polyamine catabolism enzymes, spermine oxidase (SMO) and spermidine/spermine N (1)-acetyltransferase (SSAT). However, ODC KD-induced growth inhibition could not be reversed by exogenous spermidine or overexpression of antizyme inhibitor (AZI), suggesting that regulation of ODC on cell proliferation may involve the signaling pathways independent of polyamine metabolism. In MCF7 and T47D cells, ODC KD, but not DFMO treatment, diminished the mRNA and protein expression of ERα. Overexpression of antizyme (AZ), an ODC inhibitory protein, suppressed ERα expression, suggesting that ODC plays an important role in regulation of ERα expression. Decrease of ERα expression by ODC siRNA altered the mRNA expression of a subset of ERα response genes. Our previous analysis showed that oligoamines disrupt the binding of Sp1 family members to an ERα minimal promoter element containing GC/CA-rich boxes. By using DNA affinity precipitation and mass spectrometry analysis, we identified ZBTB7A, MeCP2, PARP-1, AP2, and MAZ as co-factors of Sp1 family members that are associated with the ERα minimal promoter element. Taken together, these data provide insight into a novel antiestrogenic mechanism for polyamine biosynthesis enzymes in breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin mediates polyamine metabolism and sensitizes gastrointestinal cancer cells to antitumor polyamine-targeted therapies.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 23;13(8):e0202677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202677. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30138353 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol control of ornithine decarboxylase mRNA, enzyme activity, and polyamine levels in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: therapeutic implications.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994 Feb;29(2):189-201. doi: 10.1007/BF00665680. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994. PMID: 8012036
-
Polyamine analogues down-regulate estrogen receptor alpha expression in human breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 14;281(28):19055-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600910200. Epub 2006 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16679312 Free PMC article.
-
The antizyme family for regulating polyamines.J Biol Chem. 2018 Nov 30;293(48):18730-18735. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.003339. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30355739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational regulation of ornithine decarboxylase and other enzymes of the polyamine pathway.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999 Jan;31(1):107-22. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(98)00135-6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10216947 Review.
Cited by
-
Meditation and vacation effects have an impact on disease-associated molecular phenotypes.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Aug 30;6(8):e880. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.164. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27576169 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mga is essential for the survival of pluripotent cells during peri-implantation development.Development. 2015 Jan 1;142(1):31-40. doi: 10.1242/dev.111104. Development. 2015. PMID: 25516968 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic nucleo-cytoplasmic trafficking of proteins following exposure of MCF7 breast cancer cells to estradiol.J Proteome Res. 2014 Feb 7;13(2):1112-27. doi: 10.1021/pr4012359. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Proteome Res. 2014. PMID: 24422525 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Difluoromethylornithine, an Irreversible Inhibitor of Polyamine Biosynthesis, as a Therapeutic Strategy against Hyperproliferative and Infectious Diseases.Med Sci (Basel). 2018 Feb 8;6(1):12. doi: 10.3390/medsci6010012. Med Sci (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29419804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Epigenetic Perspective on Lifestyle Medicine for Depression: Implications for Primary Care Practice.Am J Lifestyle Med. 2020 Sep 10;16(1):76-88. doi: 10.1177/1559827620954779. eCollection 2022 Jan-Feb. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2020. PMID: 35185430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Porter CW, Herrera-Ornelas L, Pera P, Petrelli NF, Mittelman A. Polyamine biosynthetic activity in normal and neoplastic human colorectal tissues. Cancer. 1987;60(6):1275–1281. - PubMed
-
- Manni A. Polyamine involvement in breast cancer phenotype. In Vivo. 2002;16(6):493–500. - PubMed
-
- Manni A. The role of polyamines in the hormonal control of breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Treat Res. 1994;71:209–225. - PubMed
-
- Thomas T, Thomas TJ. Estradiol control of ornithine decarboxylase mRNA, enzyme activity, and polyamine levels in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: therapeutic implications. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;29(2):189–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

