Lance-adams syndrome
- PMID: 22977784
- PMCID: PMC3438425
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.561
Lance-adams syndrome
Abstract
It is not common for a patient who survives cardiac arrest to experience significant neurologic impairment such as acute and chronic post-hypoxic myoclonus, known as Lance-Adams syndrome. This syndrome is predominantly characterized by myoclonus that starts days to weeks after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in patients who regained consciousness. Although several cases of LAS were reported, the decisive treatment method has not been established. We report a 43 year old man with Lance-Adams syndrome who showed long-term improvement through treatment with anti-myoclonic agents and participation in a rehabilitation program.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Lance-Adams syndrome; Myoclonus.
Figures
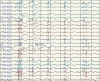
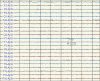

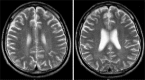
References
-
- Venkatesan A, Frucht S. Movement disorders after resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Neurol Clin. 2006;24:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Choi HC, Song HK. Is the intensive anticonvulsant treatment for control of acute posthypoxic myoclonic status epilepticus necessary? J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2006;24:125–130.
-
- Werhahn KJ, Brown P, Thompson PD, Marsden CD. The clinical features and prognosis of chronic posthypoxic myoclonus. Mov Disord. 1997;12:216–220. - PubMed
-
- Lance JW, Adams RD. The syndrome of intention or action myoclonus as a sequel to hypoxic encephalopathy. Brain. 1963;86:111–136. - PubMed
-
- Kim DH, Kim SJ, Oh KI, Kwon YS, Son BK. A Case of the successful treatment of pentobarbital for posthypoxic action myoclonus (Lance-Adams Syndrome) with refractory status epilepticus. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2006;14:342–347.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

