Inhibition by curcumin of multiple sites of the transforming growth factor-beta1 signalling pathway ameliorates the progression of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats
- PMID: 22978413
- PMCID: PMC3495222
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-156
Inhibition by curcumin of multiple sites of the transforming growth factor-beta1 signalling pathway ameliorates the progression of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats
Abstract
Background: At present there is no effective and accepted therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 signaling pathway contributes greatly to hepatic fibrosis. Reducing TGF-β synthesis or inhibiting components of its complex signaling pathway represent important therapeutic targets. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of curcumin on liver fibrosis and whether curcumin attenuates the TGF-β1 signaling pathway.
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rat was induced liver fibrosis by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) for six weeks together with or without curcumin, and hepatic histopathology and collagen content were employed to quantify liver necro-inflammation and fibrosis. Moreover, the mRNA and protein expression levels of TGF-β1, Smad2, phosphorylated Smad2, Smad3, Smad7 and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) were determined by quantitative real time-PCR, Western blot, or immunohistochemistry.
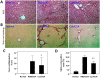
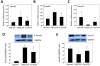
Results: Rats treated with curcumin improved liver necro-inflammation, and reduced liver fibrosis in association with decreased α-smooth muscle actin expression, and decreased collagen deposition. Furthermore, curcumin significantly attenuated expressions of TGFβ1, Smad2, phosphorylated Smad2, Smad3, and CTGF and induced expression of the Smad7.
Conclusions: Curcumin significantly attenuated the severity of CCl4-induced liver inflammation and fibrosis through inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signalling pathway and CTGF expression. These data suggest that curcumin might be an effective antifibrotic drug in the prevention of liver disease progression.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of ginseng extract on the TGF-β1 signaling pathway in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 13;17(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1507-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28086769 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 18α-glycyrrhizin on TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1292-301. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25973013 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effect of Corilagin on miR-21-Regulated Hepatic Fibrosis Signaling Pathway.Am J Chin Med. 2019;47(7):1541-1569. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X19500794. Am J Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31752524
-
Bi-directional regulation of TGF-β/Smad pathway by arsenic: A systemic review and meta-analysis of in vivo and in vitro studies.Life Sci. 2019 Mar 1;220:92-105. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.01.042. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30703382
-
Exploring the Antifibrotic Mechanisms of Ghrelin: Modulating TGF-β Signalling in Organ Fibrosis.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024 Nov 21;27:e8. doi: 10.1017/erm.2024.38. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39569809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatic stellate cell is activated by microRNA-181b via PTEN/Akt pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Jan;398(1-2):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2199-8. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25148875
-
Therapeutic targeting of liver inflammation and fibrosis by nanomedicine.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2014 Dec;3(6):364-76. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.11.02. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2014. PMID: 25568860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin downregulates the expression of Snail via suppressing Smad2 pathway to inhibit TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in hepatoma cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 21;8(65):108498-108508. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22590. eCollection 2017 Dec 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29312546 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette Smoke Contributes to the Progression of MASLD: From the Molecular Mechanisms to Therapy.Cells. 2025 Feb 4;14(3):221. doi: 10.3390/cells14030221. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39937012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol treatment ameliorates hepatic damage via the TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway in a phenobarbital/CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(9):1124-1133. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.75737.16398. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39055873 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

