A predictive tool for an effective use of (18)F-FDG PET in assessing activity of sarcoidosis
- PMID: 22978780
- PMCID: PMC3509391
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-12-57
A predictive tool for an effective use of (18)F-FDG PET in assessing activity of sarcoidosis
Abstract
Background: (18)F-FDG PET/CT (PET) is useful in assessing inflammatory activity in sarcoidosis. However, no appropriate indications are available. The aim of this study was to develop a prediction rule that can be used to identify symptomatic sarcoidosis patients who have a high probability of PET-positivity.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed a cohort of sarcoidosis patients with non organ specific persistent disabling symptoms (n = 95). Results of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) assessment and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) were included in the predefined model. HRCT scans were classified using a semi-quantitative scoring system and PET findings as positive or negative, respectively. A prediction model was derived based on logistic regression analysis. We quantified the model's performance using measures of discrimination and calibration. Finally, we constructed a prediction rule that should be easily applicable in clinical practice.
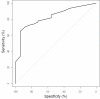
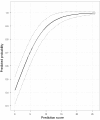
Results: The prediction rule showed good calibration and good overall performance (goodness-of-fit test, p = 0.78, Brier score 20.1%) and discriminated between patients with positive and negative PET findings (area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve, 0.83). If a positive predictive value for the presence of inflammatory activity of ≥90% is considered acceptable for clinical decision-making without referral to PET, PET would be indicated in only 29.5% of the patients. Using a positive predictive value of 98%, about half of the patients (46.3%) would require referral to PET.
Conclusions: The derived and internally validated clinical prediction rule, based on sIL-2R levels and HRCT scoring results, appeared to be useful to identify sarcoidosis patients with a high probability of inflammatory activity. Using this rule may enable a more effective use of PET scan for assessment of inflammatory activity in sarcoidosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammatory activity assessment by F18 FDG-PET/CT in persistent symptomatic sarcoidosis.Respir Med. 2011 Dec;105(12):1917-24. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2011.08.012. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Respir Med. 2011. PMID: 21899998
-
Severity of pulmonary involvement and (18)F-FDG PET activity in sarcoidosis.Respir Med. 2013 Mar;107(3):439-47. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2012.11.011. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Respir Med. 2013. PMID: 23261309
-
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography is useful for the diagnosis of intraocular sarcoidosis in patients with a normal CT scan.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Nov;103(11):1650-1655. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313133. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30658987
-
FDG-PET/CT Assessment of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: A Guide for Internists.Curr Med Imaging Rev. 2019;15(1):21-25. doi: 10.2174/1573405614666180528101755. Curr Med Imaging Rev. 2019. PMID: 31964323 Review.
-
18F-FDG PET/CT in sarcoidosis management: review and report of 20 cases.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008 Aug;35(8):1537-43. doi: 10.1007/s00259-008-0770-9. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008. PMID: 18418595 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypermetabolic Pulmonary and Mediastinal Lesions With Elevated Cancer Antigen (CA) 15-3 and CA 27-29 in a Patient With a History of Ovarian and Breast Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Mar 7;16(3):e55712. doi: 10.7759/cureus.55712. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38586673 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-quantitative metabolic values on FDG PET/CT including extracardiac sites of disease as a predictor of treatment course in patients with cardiac sarcoidosis.EJNMMI Res. 2017 Aug 18;7(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13550-017-0315-y. EJNMMI Res. 2017. PMID: 28822108 Free PMC article.
-
The Utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT for Monitoring Response and Predicting Prognosis after Glucocorticoids Therapy for Sarcoidosis.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Mar 1;2018:1823710. doi: 10.1155/2018/1823710. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29686996 Free PMC article.
-
Biological role of the soluble interleukin-2 receptor in sarcoidosis.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2017;34(2):122-129. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v34i2.5369. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2017. PMID: 32476833 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in Cardiac and Pulmonary Sarcoidosis: JACC State-of-the-Art Review.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Oct 20;76(16):1878-1901. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.08.042. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 33059834 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hunninghake GW, Costabel U, Ando M, Baughman R, Cordier JF, du Bois R, Eklund A, Kitaichi M, Lynch J, Rizzato G. et al.ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 1999;16:149–73. - PubMed
-
- Baughman RP, Lower EE, Drent M. Inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in sarcoidosis: who, what, and how to use them. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2008;25:76–89. - PubMed
-
- Consensus conference: activity of sarcoidosis. Third WASOG meeting, Los Angeles, USA, September 8-11, 1993. Eur Respir J. 1994;7:624–7. - PubMed
-
- Keijsers RG, Verzijlbergen JF, van Diepen DM, van den Bosch JM, Grutters JC. 18 F-FDG PET in sarcoidosis: an observational study in 12 patients treated with infliximab. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2008;25:143–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources