Further evidence that pediatric-onset bipolar disorder comorbid with ADHD represents a distinct subtype: results from a large controlled family study
- PMID: 22979994
- PMCID: PMC3501568
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.08.002
Further evidence that pediatric-onset bipolar disorder comorbid with ADHD represents a distinct subtype: results from a large controlled family study
Abstract
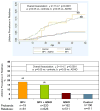
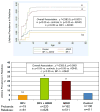
We used familial risk analysis to clarify the diagnostic comorbidity between pediatric BP-I disorder and ADHD, testing the hypothesis that pediatric-BP-I disorder comorbid with ADHD represents a distinct subtype. Structured diagnostic interviews were used to obtain DSM-IV psychiatric diagnoses on first-degree relatives (n = 726) of referred children and adolescents satisfying diagnostic criteria for BP-I disorder (n = 239). For comparison, diagnostic information on the first-degree relatives (N = 511) of non-bipolar ADHD children (N = 162) and the first degree relatives (N = 411) of control children (N = 136) with neither ADHD nor BP-I disorder were examined. BP-I disorder and ADHD in probands bred true irrespective of the comorbidity with the other disorder. We also found that the comorbid condition of BP-I disorder plus ADHD also bred true in families, and the two disorders co-segregated among relatives. This large familial risk analysis provides compelling evidence that pediatric BP-I disorder comorbid with ADHD represents a distinct familial subtype.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Asherson P, Brookes K, Franke B, Chen W, Gill M, Ebstein RP, Buitelaar J, Banaschewski T, Sonuga-Barke E, Eisenberg J, Manor I, Miranda A, Oades RD, Roeyers H, Rothenberger A, Sergeant J, Steinhausen HC, Faraone SV. Confirmation that a specific haplotype of the dopamine transporter gene is associated with combined-type ADHD. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(4):674–677. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi S, Cortese S, Solanto M, Hollander E, Pallanti S. Bipolar disorder and comorbid attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. A distinct clinical phenotype? Clinical characteristics and temperamental traits. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2010;11(4):656–666. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV, Keenan K, Benjamin J, Krifcher B, Moore C, Sprich-Buckminster S, Ugaglia K, Jellinek MS, Steingard R, Spencer T, Norman D, Kolodny R, Kraus I, Perrin J, Keller MB, Tsuang MT. Further evidence for family-genetic risk factors in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Patterns of comorbidity in probands and relatives in psychiatrically and pediatrically referred samples. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992;49(9):728–738. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV, Mick E, Williamson S, Wilens TE, Spencer TJ, Weber W, Jetton J, Kraus I, Pert J, Zallen B. Clinical correlates of ADHD in females: findings from a large group of girls ascertained from pediatric and psychiatric referral sources. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1999;38(8):966–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical