Microbiota regulate intestinal absorption and metabolism of fatty acids in the zebrafish
- PMID: 22980325
- PMCID: PMC3517662
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.003
Microbiota regulate intestinal absorption and metabolism of fatty acids in the zebrafish
Abstract
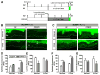
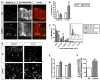
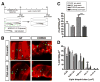
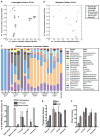
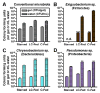
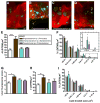
Regulation of intestinal dietary fat absorption is critical to maintaining energy balance. While intestinal microbiota clearly impact the host's energy balance, their role in intestinal absorption and extraintestinal metabolism of dietary fat is less clear. Using in vivo imaging of fluorescent fatty acid (FA) analogs delivered to gnotobiotic zebrafish hosts, we reveal that microbiota stimulate FA uptake and lipid droplet (LD) formation in the intestinal epithelium and liver. Microbiota increase epithelial LD number in a diet-dependent manner. The presence of food led to the intestinal enrichment of bacteria from the phylum Firmicutes. Diet-enriched Firmicutes and their products were sufficient to increase epithelial LD number, whereas LD size was increased by other bacterial types. Thus, different members of the intestinal microbiota promote FA absorption via distinct mechanisms. Diet-induced alterations in microbiota composition might influence fat absorption, providing mechanistic insight into how microbiota-diet interactions regulate host energy balance.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
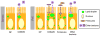
Comment in
-
Gut microbes make for fattier fish.Cell Host Microbe. 2012 Sep 13;12(3):259-61. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.006. Cell Host Microbe. 2012. PMID: 22980321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babin PJ, Vernier JM. Plasma lipoproteins in fish. J Lipid Res. 1989;30(4):467–489. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Statist Soc B. 1995;57(1):289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK078669/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HG4872/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK093399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK093399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081426/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM095385/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004872/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 GM063904/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK091129/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- GM63904/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK081426/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004866/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM095385/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK093399/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM141804/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HG4866/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063904/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK78669/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DK091129/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

