Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing
- PMID: 22980975
- PMCID: PMC3557932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.029
Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing
Abstract
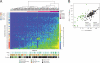
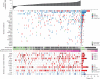
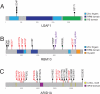
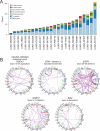
Lung adenocarcinoma, the most common subtype of non-small cell lung cancer, is responsible for more than 500,000 deaths per year worldwide. Here, we report exome and genome sequences of 183 lung adenocarcinoma tumor/normal DNA pairs. These analyses revealed a mean exonic somatic mutation rate of 12.0 events/megabase and identified the majority of genes previously reported as significantly mutated in lung adenocarcinoma. In addition, we identified statistically recurrent somatic mutations in the splicing factor gene U2AF1 and truncating mutations affecting RBM10 and ARID1A. Analysis of nucleotide context-specific mutation signatures grouped the sample set into distinct clusters that correlated with smoking history and alterations of reported lung adenocarcinoma genes. Whole-genome sequence analysis revealed frequent structural rearrangements, including in-frame exonic alterations within EGFR and SIK2 kinases. The candidate genes identified in this study are attractive targets for biological characterization and therapeutic targeting of lung adenocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cancer Statistics. W.H. Organization; 2004.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

