A population-based study of autosomal-recessive disease-causing mutations in a founder population
- PMID: 22981120
- PMCID: PMC3484657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.08.007
A population-based study of autosomal-recessive disease-causing mutations in a founder population
Abstract
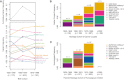
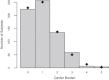
The decreasing cost of whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing has resulted in a renaissance for identifying Mendelian disease mutations, and for the first time it is possible to survey the distribution and characteristics of these mutations in large population samples. We conducted carrier screening for all autosomal-recessive (AR) mutations known to be present in members of a founder population and revealed surprisingly high carrier frequencies for many of these mutations. By utilizing the rich demographic, genetic, and phenotypic data available on these subjects and simulations in the exact pedigree that these individuals belong to, we show that the majority of mutations were most likely introduced into the population by a single founder and then drifted to the high carrier frequencies observed. We further show that although there is an increased incidence of AR diseases overall, the mean carrier burden is likely to be lower in the Hutterites than in the general population. Finally, on the basis of simulations, we predict the presence of 30 or more undiscovered recessive mutations among these subjects, and this would at least double the number of AR diseases that have been reported in this isolated population.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Peltonen L. Molecular background of the Finnish disease heritage. Ann. Med. 1997;29:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Sheffield V.C., Stone E.M., Carmi R. Use of isolated inbred human populations for identification of disease genes. Trends Genet. 1998;14:391–396. - PubMed
-
- Arcos-Burgos M., Muenke M. Genetics of population isolates. Clin. Genet. 2002;61:233–247. - PubMed
-
- McKusick V.A. Genetic studies in American inbred populations with particular reference to the Old Order Amish. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1973;9:1276–1284. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Perez V.L., Ide S.E., Strom T.M., Lorenz B., Wilson D., Woods K., King L., Francomano C., Freisinger P., Spranger S. Mutations in a new gene in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome and Weyers acrodental dysostosis. Nat. Genet. 2000;24:283–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

