Protective role of clusterin in preserving endothelial function in AL amyloidosis
- PMID: 22981431
- PMCID: PMC3478430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.08.028
Protective role of clusterin in preserving endothelial function in AL amyloidosis
Abstract
Misfolded immunoglobulin light chain proteins (LC) in light chain amyloidosis (AL) are toxic to vascular tissues. We tested the hypothesis that chaperone protein clusterin preserves endothelial function and cell survival during LC exposure.
Methods: LC (20 μg/mL) were given to human aortic endothelial cells (EC) for 24-h and clusterin protein/gene expression and secretion were measured. DNA fragmentation was measured with/without recombinant clusterin (Clu, 300 ng/mL). Adipose arterioles (non-AL subjects) were tested for dilator responses to acetylcholine/papaverine at baseline and after 1-h of LC ± Clu.
Results: LC reduced EC clusterin secretion, protein and gene expression while increasing DNA fragmentation. Clu attenuated LC-induced DNA fragmentation and restored dilator response to acetylcholine (logEC50: control -7.05 ± 0.2, LC + Clu -6.53 ± 0.4, LC -4.28 ± 0.7, p < 0.05 versus control, LC + Clu).
Conclusions: LC induced endothelial cell death and dysfunction while reducing clusterin protein/gene expression and secretion. Exogenous clusterin attenuated LC toxicity. This represents a new pathobiologic mechanism and therapeutic target for AL amyloidosis.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures
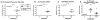

Similar articles
-
PEGylated-nanoliposomal clusterin for amyloidogenic light chain-induced endothelial dysfunction.J Liposome Res. 2018 Jun;28(2):97-105. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2016.1274756. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Liposome Res. 2018. PMID: 28103719 Free PMC article.
-
Human microvascular dysfunction and apoptotic injury induced by AL amyloidosis light chain proteins.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):H2305-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00503.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21963839 Free PMC article.
-
Monosialoganglioside-Containing Nanoliposomes Restore Endothelial Function Impaired by AL Amyloidosis Light Chain Proteins.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Jun 13;5(6):e003318. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003318. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27412900 Free PMC article.
-
CLU "in and out": looking for a link.Adv Cancer Res. 2009;105:93-113. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(09)05006-4. Adv Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19879425 Review.
-
Beyond the plasma cell: emerging therapies for immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis.Blood. 2016 May 12;127(19):2275-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-681650. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26907632 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoliposomes protect against AL amyloid light chain protein-induced endothelial injury.J Liposome Res. 2014 Mar;24(1):69-73. doi: 10.3109/08982104.2013.838258. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Liposome Res. 2014. PMID: 24236475 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoliposomes protect against human arteriole endothelial dysfunction induced by β-amyloid peptide.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016 Feb;36(2):405-12. doi: 10.1177/0271678X15610134. Epub 2015 Oct 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016. PMID: 26661197 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Pathophysiological Insights Into Immunological Mediated Glomerular Diseases in Childhood.Front Pediatr. 2020 May 12;8:205. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00205. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32478016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose and leptomeningeal arteriole endothelial dysfunction induced by β-amyloid peptide: a practical human model to study Alzheimer's disease vasculopathy.J Neurosci Methods. 2014 Sep 30;235:123-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.06.014. Epub 2014 Jul 5. J Neurosci Methods. 2014. PMID: 25004204 Free PMC article.
-
Clusterin knockdown has effects on intracellular and secreted von Willebrand factor in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 16;19(2):e0298133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298133. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38363768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schrijvers EM, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Breteler MM. Plasma clusterin and the risk of Alzheimer disease. JAMA. 305:1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Yerbury JJ, Poon S, Meehan S, Thompson B, Kumita JR, Dobson CM, Wilson MR. The extracellular chaperone clusterin influences amyloid formation and toxicity by interacting with prefibrillar structures. FASEB J. 2007;21:2312–2322. - PubMed
-
- Berghoff M, Kathpal M, Khan F, Skinner M, Falk R, Freeman R. Endothelial dysfunction precedes C-fiber abnormalities in primary (AL) amyloidosis. Ann Neurol. 2003;53:725–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

