Oxidized high-density lipoprotein is associated with increased plasma glucose in non-diabetic dyslipidemic subjects
- PMID: 22981508
- PMCID: PMC5555586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.08.021
Oxidized high-density lipoprotein is associated with increased plasma glucose in non-diabetic dyslipidemic subjects
Abstract
Background: Oxidized high-density lipoprotein (oxHDL) has reduced capacity for cholesterol efflux and some of other anti-atherogenic properties of HDL, but the role of oxHDL in the pathogenesis of cardiometabolic disease has not been fully demonstrated. This study investigated the association of oxHDL with plasma glucose (PG) and the other atherosclerotic risk variables in non-diabetic dyslipidemic subjects.
Methods: Conventional atherosclerotic markers and LDL particle size (LDL-PS), as determined by gel electrophoresis, were measured in 155 non-diabetic subjects (mean age of 57 years) with dyslipidemia. Serum oxHDL levels were quantified using an antibody against oxidized human apoA-I in a sandwich ELISA format.
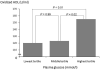
Results: Multiple regression analysis adjusted for possible confounders revealed that HDL-cholesterol was independently, significantly and positively correlated with LDL-PS and oxHDL. By multiple regression analysis, oxHDL was independently, significantly and positively correlated with fasting PG (β=0.19, P=0.01). Subjects in the highest PG tertile group had approximately 30% higher oxHDL levels than the lowest PG tertile group.
Conclusions: These results suggest that high PG levels may contribute to the HDL oxidation, irrespective of HDL-cholesterol levels, even in non-diabetic subjects with dyslipidemia, and that the measurement of oxHDL may be a useful marker of dysfunctional HDL.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Deaton C, Froelicher ES, Wu LH, Ho C, Shishani K, Jaarsma T. The global burden of cardiovascular disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2011;10:S5–13. - PubMed
-
- Davidson MH. Focusing on high-density lipoprotein for coronary heart disease risk reduction. Cardiol Clin. 2011;29:105–22. - PubMed
-
- Navab M, Reddy ST, Van Lenten BJ, Fogelman AM. HDL and cardiovascular disease: atherogenic and atheroprotective mechanisms. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;8:222–32. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima T, Origuchi N, Matsunaga T, Kawai S, Hokari S, Nakamura H, et al. Localization of oxidized HDL in atheromatous plaques and oxidized HDL binding sites on human aortic endothelial cells. Ann Clin Biochem. 2000;37:179–86. - PubMed
-
- Thorne RF, Mhaidat NM, Ralston KJ, Burns GF. CD36 is a receptor for oxidized high density lipoprotein: implications for the development of atherosclerosis. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:1227–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

