Dynamic and coordinated epigenetic regulation of developmental transitions in the cardiac lineage
- PMID: 22981692
- PMCID: PMC3462286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.035
Dynamic and coordinated epigenetic regulation of developmental transitions in the cardiac lineage
Abstract
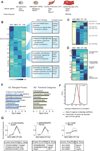
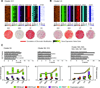
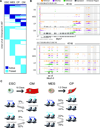
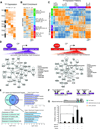
Heart development is exquisitely sensitive to the precise temporal regulation of thousands of genes that govern developmental decisions during differentiation. However, we currently lack a detailed understanding of how chromatin and gene expression patterns are coordinated during developmental transitions in the cardiac lineage. Here, we interrogated the transcriptome and several histone modifications across the genome during defined stages of cardiac differentiation. We find distinct chromatin patterns that are coordinated with stage-specific expression of functionally related genes, including many human disease-associated genes. Moreover, we discover a novel preactivation chromatin pattern at the promoters of genes associated with heart development and cardiac function. We further identify stage-specific distal enhancer elements and find enriched DNA binding motifs within these regions that predict sets of transcription factors that orchestrate cardiac differentiation. Together, these findings form a basis for understanding developmentally regulated chromatin transitions during lineage commitment and the molecular etiology of congenital heart disease.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Maps for changing landscapes: viewing epigenomic signatures through differentiation.Cell Stem Cell. 2012 Nov 2;11(5):581-2. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.10.009. Cell Stem Cell. 2012. PMID: 23122282
-
An epigenetic roadmap for cardiomyocyte differentiation.Circ Res. 2013 Mar 15;112(6):881-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.301134. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23493303 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

