Functional imaging of the thalamus in language
- PMID: 22981716
- PMCID: PMC4836874
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandl.2012.06.004
Functional imaging of the thalamus in language
Abstract
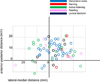
Herein, the literature regarding functional imaging of the thalamus during language tasks is reviewed. Fifty studies met criteria for analysis. Two of the most common task paradigms associated with thalamic activation were generative tasks (e.g. word or sentence generation) and naming, though activation was also seen in tasks that involve lexical decision, reading and working memory. Typically, thalamic activation was seen bilaterally, left greater than right, along with activation in frontal and temporal cortical regions. Thalamic activation was seen with perceptually challenging tasks, though few studies rigorously correlated thalamic activation with measures of attention or task difficulty. The peaks of activation loci were seen in virtually all thalamic regions, with a bias towards left-sided and midline activation. These analyses suggest that the thalamus may be involved in processes that involve manipulations of lexical information, but point to the need for more systematic study of the thalamus using language tasks.
Copyright © 2012. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
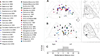
Similar articles
-
Lateralized and Region-Specific Thalamic Processing of Lexical Status during Reading Aloud.J Neurosci. 2022 Apr 13;42(15):3228-3240. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1332-21.2022. Epub 2022 Mar 1. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35232766 Free PMC article.
-
The thalamus and language revisited.Brain Lang. 2013 Jul;126(1):99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2012.06.010. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Brain Lang. 2013. PMID: 22857902 Review.
-
Subcortical mechanisms in language: lexical-semantic mechanisms and the thalamus.Brain Cogn. 1999 Jul;40(2):414-38. doi: 10.1006/brcg.1999.1088. Brain Cogn. 1999. PMID: 10413568
-
Thalamic mechanisms in language: a reconsideration based on recent findings and concepts.Brain Lang. 2013 Jul;126(1):73-88. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2012.06.011. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Brain Lang. 2013. PMID: 22831779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the human thalamus in language and memory: evidence from electrophysiological studies.Brain Cogn. 2000 Mar;42(2):218-30. doi: 10.1006/brcg.1999.1101. Brain Cogn. 2000. PMID: 10744921
Cited by
-
Thalamic Aphasia: a Review.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022 Dec;22(12):855-865. doi: 10.1007/s11910-022-01242-2. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36383308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticothalamic Pathways in Auditory Processing: Recent Advances and Insights From Other Sensory Systems.Front Neural Circuits. 2021 Aug 19;15:721186. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2021.721186. eCollection 2021. Front Neural Circuits. 2021. PMID: 34489648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in the Treatment of Subacute Post-Stroke Thalamic Aphasia.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020 Sep 3;7(11):001794. doi: 10.12890/2020_001794. eCollection 2020. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 33194851 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Navigated Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: New Insight for Brain Tumor-Related Language Mapping.J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 27;12(10):1589. doi: 10.3390/jpm12101589. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36294728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurobiology of taboo language processing: fMRI evidence during spoken word production.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2019 Mar 5;14(3):271-279. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsz009. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30715549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alain C, Reinke K, McDonald KL, Chau W, Tam F, Pacurar A, et al. Left thalamo-cortical network implicated in successful speech separation and identification. NeuroImage. 2005;26(2):592–599. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.02.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrew J, Watkins E. A variability study. Williams and Wilkins; 1969. A stereotactic atlas of the human thalamus and adjacent structures.
-
- Archer C, Ilinsky I, Goldfader P, Smith K. Case report. Aphasia in thalamic stroke: CT stereotactic localization. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 1981;5(3):427–432. - PubMed
-
- Assaf M, Calhoun VD, Kuzu CH, Kraut MA, Rivkin PR, Hart J, Jr, et al. Neural correlates of the object-recall process in semantic memory. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging. 2006;147(2–3):115–126. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2006.01.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baker S, Frith C, Dolan R. The interaction between mood and cognitive function studied with PET. Psychological Medicine. 1997;27:565–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

