The involvement of Reelin in neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 22981949
- PMCID: PMC3632377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.08.015
The involvement of Reelin in neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
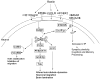
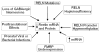
Reelin is a glycoprotein that serves important roles both during development (regulation of neuronal migration and brain lamination) and in adulthood (maintenance of synaptic function). A number of neuropsychiatric disorders including autism, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, Alzheimer's disease and lissencephaly share a common feature of abnormal Reelin expression in the brain. Altered Reelin expression has been hypothesized to impair neuronal connectivity and synaptic plasticity, leading ultimately to the cognitive deficits present in these disorders. The mechanisms for abnormal Reelin expression in some of these disorders are currently unknown although possible explanations include early developmental insults, mutations, hypermethylation of the promoter for the Reelin gene (RELN), miRNA silencing of Reelin mRNA, FMRP underexpression and Reelin processing abnormalities. Increasing Reelin expression through pharmacological therapies may help ameliorate symptoms resulting from Reelin deficits. This article is part of the Special Issue entitled 'Neurodevelopmental Disorders'.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Smith CL, Farone SV, Shafa R, Stone W, Glatt SJ, Tsuang MT. Methylomics in psychiatry: modulation of gene-environment interactions may be through DNA methylation. Am J Med Genet. 2004;127B:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, Shafa R, Glatt SJ, Nguyen G, Ponte JF, Thiagalingam S, Tsuang MT. Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of schizophrenic patients: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;134B:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Abraham H, Meyer G. Reelin-expressing neurons in the postnatal and adult human hippocampal formation. Hippocampus. 2003;13:715–727. - PubMed
-
- Akahane A, Kunugi H, Tanaka H, Nanko S. Association analysis of polymorphic CGG repeat in 5′ UTR of the reelin and VLDLR genes with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2002;58:37–41. - PubMed
-
- Akbarian S, Bunney WE, Jr, Potkin SG, Wigal SB, Hagman JO, Sandman CA, Jones EG. Altered distribution of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-diaphorase cells in frontal lobe of schizophrenics implies disturbances of cortical development. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1993;50:169–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

