An indirect role for oncomir-519b in the expression of truncated neurokinin-1 in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 22981979
- PMCID: PMC3645290
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.09.002
An indirect role for oncomir-519b in the expression of truncated neurokinin-1 in breast cancer cells
Abstract
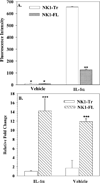
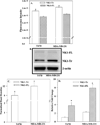
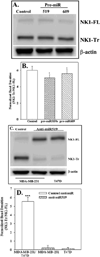
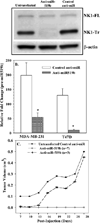
Neurokinin 1 (NK1) encodes full-length (NK1-FL) and truncated (NK1-Tr) receptors, with distinct 3' UTR. NK1-Tr exerts oncogenic functions and is increased in breast cancer (BC). Enhanced transcription of NK1 resulted in higher level of NK1-Tr. The 3' UTR of these two transcripts are distinct with NK1-Tr terminating at a premature stop codon. NK1-Tr mRNA gained an advantage over NK1-FL with regards to translation. This is due to the ability of miR519B to interact with sequences within the 3' UTR of NK1-FL, but not NK1-Tr since the corresponding region is omitted. MiR519b suppressed the translation of NK1-FL in T47D and MDA-MB-231 resulting in increased NK1-Tr protein. Cytokines can induce the transcription of NK1. However, our studies indicated that translation appeared to be independent of cytokine production by the BC cells (BCCs). This suggested that transcription and translation of NK1 might be independent. The findings were validated in vivo. MiR-519b suppressed the growth of MDA-MB-231 in 7/10 nude BALB/c. In total, increased NK1-Tr in BCCs is due to enhanced transcription and suppressed translation of NK1-FL by miR-519b to reduced tumor growth. In summary, we report on miRNA as a method to further regulate the expression of a spiced variant to promote oncogenesis. In addition, the findings have implications for therapy with NK1 antagonists. The oncogenic effect of NK1-Tr must be considered to improve the efficacy of current drugs to NK1.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures



References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;61:133–134. - PubMed
-
- Munoz M, Rosso M, Covenas R. A new frontier in the treatment of cancer: NK-1 receptor antagonists. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17:504–516. - PubMed
-
- Brener S, Gonzalez-Moles MA, Tostes D, Esteban F, Gil-Montoya JA, Ruiz-Avila I, Bravo M, Munoz M. A role for the substance P/NK-1 receptor complex in cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:2323–2329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

