Modulation of methamphetamine-induced nitric oxide production by neuropeptide Y in the murine striatum
- PMID: 22982589
- PMCID: PMC4012334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.09.013
Modulation of methamphetamine-induced nitric oxide production by neuropeptide Y in the murine striatum
Abstract
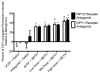
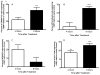
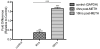
Methamphetamine (METH) is a potent stimulant that induces both acute and long-lasting neurochemical changes in the brain including neuronal cell loss. Our laboratory demonstrated that the neuropeptide substance P enhances the striatal METH-induced production of nitric oxide (NO). In order to better understand the role of the striatal neuropeptides on the METH-induced production of NO, we used agonists and antagonists of the NPY (Y1R and Y2R) receptors infused via intrastriatal microinjection followed by a bolus of METH (30 mg/kg, ip) and measured 3-NT immunofluorescence, an indirect index of NO production. One striatum received pharmacological agent while the contralateral striatum received aCSF and served as control. NPY receptor agonists dose dependently attenuated the METH-induced production of striatal 3-NT. Conversely, NPY receptor antagonists had the opposite effect. Moreover, METH induced the accumulation of cyclic GMP and activated caspase-3 in approximately 18% of striatal neurons, a phenomenon that was attenuated by pre-treatment with NPY2 receptor agonist. Lastly, METH increased the levels of striatal preproneuropeptide Y mRNA nearly five-fold 16 h after injection as determined by RT-PCR, suggesting increased utilization of the neuropeptide. In conclusion, NPY inhibits the METH-induced production of NO in striatal tissue. Consequently, production of this second messenger induces the accumulation of cyclic GMP and activated caspase-3 in some striatal neurons, an event that may precede the apoptosis of some striatal neurons.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abekawa T, Ohmori T, Koyama T. Effect of NO synthesis inhibition on striatal dopamine release and stereotyped behavior induced by a single administration of methamphetamine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1997;5:831–838. - PubMed
-
- Adrian TE, Allen JM, Bloom SR, Ghatei MA, Rossor MN, Roberts GW, Crow TJ, Tatemoto K, Polak JM. Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature. 1983;306:584–586. - PubMed
-
- Ariano MA, Grissell AE, Littlejohn FC, Buchanan TM, Elsworth JD, Collier TJ, Steece-Collier K. Partial dopamine loss enhances activated caspase-3 activity: differential outcomes in striatal projection neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2005;82:387–396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

