Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-B signaling
- PMID: 22983209
- PMCID: PMC3458152
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3212
Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-B signaling
Abstract
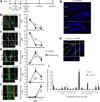
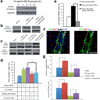
Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus involves activation of quiescent neural stem cells (NSCs) to yield transiently amplifying NSCs, progenitors, and, ultimately, neurons that affect learning and memory. This process is tightly controlled by microenvironmental cues, although a few endogenous factors are known to regulate neuronal differentiation. Astrocytes have been implicated, but their role in juxtacrine (that is, cell-cell contact dependent) signaling in NSC niches has not been investigated. We found that ephrin-B2 presented from rodent hippocampal astrocytes regulated neurogenesis in vivo. Furthermore, clonal analysis in NSC fate-mapping studies revealed a previously unknown role for ephrin-B2 in instructing neuronal differentiation. In addition, ephrin-B2 signaling, transduced by EphB4 receptors on NSCs, activated β-catenin in vitro and in vivo independently of Wnt signaling and upregulated proneural transcription factors. Ephrin-B2(+) astrocytes therefore promote neuronal differentiation of adult NSCs through juxtacrine signaling, findings that advance our understanding of adult neurogenesis and may have future regenerative medicine implications.
Figures
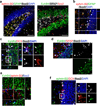
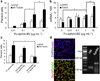
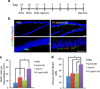

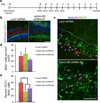
References
-
- Eriksson PS, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998;4:1313–1317. - PubMed
-
- Lois C, Alvarez-Buylla A. Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science. 1994;264:1145–1148. - PubMed
-
- Spalding KL, Bhardwaj RD, Buchholz BA, Druid H, Frisén J. Retrospective birth dating of cells in humans. Cell. 2005;122:133–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

