Genetic disruption of protein kinase Cδ reduces endotoxin-induced lung injury
- PMID: 22983354
- PMCID: PMC3517673
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00169.2012
Genetic disruption of protein kinase Cδ reduces endotoxin-induced lung injury
Abstract
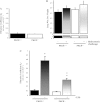
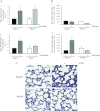
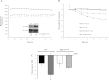
The pathogenesis of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by sequestration of leukocytes in lung tissue, disruption of capillary integrity, and pulmonary edema. PKCδ plays a critical role in RhoA-mediated endothelial barrier function and inflammatory responses. We used mice with genetic deletion of PKCδ (PKCδ(-/-)) to assess the role of PKCδ in susceptibility to LPS-induced lung injury and pulmonary edema. Under baseline conditions or in settings of increased capillary hydrostatic pressures, no differences were noted in the filtration coefficients (k(f)) or wet-to-dry weight ratios between PKCδ(+/+) and PKCδ(-/-) mice. However, at 24 h after exposure to LPS, the k(f) values were significantly higher in lungs isolated from PKCδ(+/+) than PKCδ(-/-) mice. In addition, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid obtained from LPS-exposed PKCδ(+/+) mice displayed increased protein and cell content compared with LPS-exposed PKCδ(-/-) mice, but similar changes in inflammatory cytokines were measured. Histology indicated elevated LPS-induced cellularity and inflammation within PKCδ(+/+) mouse lung parenchyma relative to PKCδ(-/-) mouse lungs. Transient overexpression of catalytically inactive PKCδ cDNA in the endothelium significantly attenuated LPS-induced endothelial barrier dysfunction in vitro and increased k(f) lung values in PKCδ(+/+) mice. However, transient overexpression of wild-type PKCδ cDNA in PKCδ(-/-) mouse lung vasculature did not alter the protective effects of PKCδ deficiency against LPS-induced acute lung injury. We conclude that PKCδ plays a role in the pathological progression of endotoxin-induced lung injury, likely mediated through modulation of inflammatory signaling and pulmonary vascular barrier function.
Figures

References
-
- Bai X, Margariti A, Hu Y, Sato Y, Zeng L, Ivetic A, Habi O, Mason JC, Wang X, Xu Q. Protein kinase Cδ deficiency accelerates neointimal lesions of mouse injured artery involving delayed reendothelialization and vasohibin-1 accumulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30: 2467–2474, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bair AM, Thippegowda PB, Freichel M, Cheng N, Ye RD, Vogel SM, Yu Y, Flockerzi V, Malik AB, Tiruppathi C. Ca2+ entry via TRPC channels is necessary for thrombin-induced NF-κB activation in endothelial cells through AMP-activated protein kinase and protein kinase Cδ. J Biol Chem 284: 563–574, 2009 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bey EA, Xu B, Bhattacharjee A, Oldfield CM, Zhao X, Li Q, Subbulakshmi V, Feldman GM, Wientjes FB, Cathcart MK. Protein kinase Cδ is required for p47phox phosphorylation and translocation in activated human monocytes. J Immunol 173: 5730–5738, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Brigham KL, Meyrick B. Endotoxin and lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis 133: 913–927, 1986 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

