p21-Activated kinase 1 is required for efficient tumor formation and progression in a Ras-mediated skin cancer model
- PMID: 22983922
- PMCID: PMC3500416
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2246
p21-Activated kinase 1 is required for efficient tumor formation and progression in a Ras-mediated skin cancer model
Abstract
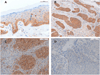
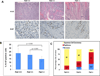
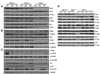
The RAS genes are the most commonly mutated oncogenes in human cancer and present a particular therapeutic dilemma, as direct targeting of Ras proteins by small molecules has proved difficult. Signaling pathways downstream of Ras, in particular Raf/Mek/Erk and PI3K/Akt/mTOR, are dominated by lipid and protein kinases that provide attractive alternate targets in Ras-driven tumors. As p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1) has been shown to regulate both these signaling pathways and is itself upregulated in many human cancers, we assessed the role of Pak1 in Ras-driven skin cancer. In human squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), we found a strong positive correlation between advanced stage and grade and PAK1 expression. Using a mouse model of Kras-driven SCC, we showed that deletion of the mouse Pak1 gene led to markedly decreased tumorigenesis and progression, accompanied by near total loss of Erk and Akt activity. Treatment of Kras(G12D) mice with either of two distinct small molecule Pak inhibitors (PF3758309 and FRAX597) caused tumor regression and loss of Erk and Akt activity. Tumor regression was also seen in mice treated with a specific Mek inhibitor, but not with an Akt inhibitor. These findings establish Pak1 as a new target in KRAS-driven tumors and suggest a mechanism of action through the Erk, but not the Akt, signaling pathway.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests: none
Figures


References
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer research. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Eberhard DA, Johnson BE, Amler LC, Goddard AD, Heldens SL, Herbst RS, et al. Mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor and in KRAS are predictive and prognostic indicators in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with chemotherapy alone and in combination with erlotinib. J Clin Onc. 2005;23:5900–5909. - PubMed
-
- Cox AD, Der CJ. Ras family signaling: therapeutic targeting. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002;1:599–606. - PubMed
-
- Downward J. Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Matallanas D, Crespo P. New druggable targets in the Ras pathway? Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2010;12:674–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

