Boswellic acid exerts antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of the let-7 and miR-200 microRNA family
- PMID: 22983985
- PMCID: PMC3510738
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgs286
Boswellic acid exerts antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of the let-7 and miR-200 microRNA family
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a complex disease with genetic and epigenetic alterations in many key oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. The active principle of a gum resin from Boswellia serrata, 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid (AKBA), has recently gained attention as a chemopreventive compound due to its ability to target key oncogenic proteins such as 5-lipoxygenase and nuclear factor-kappaB. AKBA has been shown to inhibit the growth of CRC cells; however, the precise molecular mechanisms underlying its anticancer activities in CRC remain unclear. We hypothesized that boswellic acids may achieve their chemopreventive effects by modulating specific microRNA (miRNA) pathways. We found that AKBA significantly up-regulated expression of the let-7 and miR-200 families in various CRC cell lines. Both let-7 and miR-200 are putative tumor-suppressive miRNAs. AKBA modulated the expression of several downstream targets of the let-7 and miR-200 families, such as CDK6, vimentin and E-cadherin. These data were further strengthened by miRNA knockdown studies, which revealed that inhibition of let-7i facilitated enhanced cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. In addition, AKBA also induced similar modulation of the let-7 and miR-200 downstream genes in CRC tumors orthotopically implanted in nude mice. These results indicate that AKBA-induced antitumor effects in CRC occur, at least partly through the up-regulation of specific miRNA pathways. Our data provide novel evidence that anticancer effects of boswellic acids are due in part to their ability to regulate cellular epigenetic machinery and further highlight the promise for this phytochemical in the preventative and therapeutic applications of CRC.
Figures
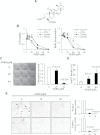

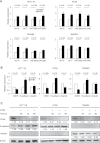
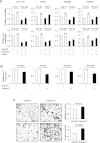
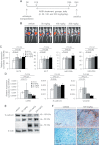
References
-
- Jemal A., et al. (2010). Cancer statistics, 2010. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 60 277–300 - PubMed
-
- Jemal A., et al. (2011). Global cancer statistics. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 61 69–90 - PubMed
-
- Calin G.A., et al. (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6 857–866 - PubMed
-
- Garzon R., et al. (2009). MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 60 167–179 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

