Investigations of human platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase: role of lipoxygenase products in platelet activation
- PMID: 22984144
- PMCID: PMC3494251
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M026385
Investigations of human platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase: role of lipoxygenase products in platelet activation
Abstract
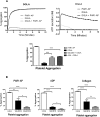
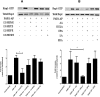
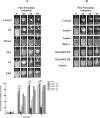
Human platelet-type 12-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) has recently been shown to play an important role in regulation of human platelet function by reacting with arachidonic acid (AA). However, a number of other fatty acids are present on the platelet surface that, when cleaved from the phospholipid, can be oxidized by 12-LOX. We sought to characterize the substrate specificity of 12-LOX against six essential fatty acids: AA, dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), α-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosadienoic acid (EDA), and linoleic acid (LA). Three fatty acids were comparable substrates (AA, DGLA, and EPA), one was 5-fold slower (ALA), and two showed no reactivity with 12-LOX (EDA and LA). The bioactive lipid products resulting from 12-LOX oxidation of DGLA, 12-(S)-hydroperoxy-8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatrienoic acid [12(S)-HPETrE], and its reduced product, 12(S)-HETrE, resulted in significant attenuation of agonist-mediated platelet aggregation, granule secretion, αIIbβ3 activation, Rap1 activation, and clot retraction. Treatment with DGLA similarly inhibited PAR1-mediated platelet activation as well as platelet clot retraction. These observations are in surprising contrast to our recent work showing 12(S)-HETE is a prothrombotic bioactive lipid and support our hypothesis that the overall effect of 12-LOX oxidation of fatty acids in the platelet is dependent on the fatty acid substrates available at the platelet membrane.
Figures




References
-
- Solomon E. I., Zhou J., Neese F., Pavel E. G. 1997. New insights from spectroscopy into the structure/function relationships of lipoxygenases. Chem. Biol. 4: 795–808 - PubMed
-
- Serhan C. N. 1994. Lipoxin biosynthesis and its impact in inflammatory and vascular events. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1212: 1–25 - PubMed
-
- Nakano H., Inoue T., Kawasaki N., Miyataka H., Matsumoto H., Taguchi T., Inagaki N., Nagai H., Satoh T. 2000. Synthesis and biological activities of novel antiallergic agents with 5-lipoxygenase inhibiting action. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8: 373–380 - PubMed
-
- Steele V. E., Holmes C. A., Hawk E. T., Kopelovich L., Lubet R. A., Crowell J. A., Sigman C. C., Kelloff G. J. 1999. Lipoxygenase inhibitors as potential cancer chemopreventives. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 8: 467–483 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

