Hypomorphic sialidase expression decreases serum cholesterol by downregulation of VLDL production in mice
- PMID: 22984145
- PMCID: PMC3494259
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M027300
Hypomorphic sialidase expression decreases serum cholesterol by downregulation of VLDL production in mice
Abstract
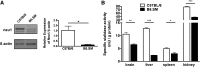
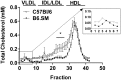
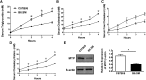
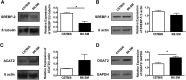
Lipoprotein metabolism is an important contributing factor in the development and progression of atherosclerosis. Plasma lipoproteins and their receptors are heavily glycosylated and sialylated, and levels of sialic acids modulate their biological functions. Sialylation is controlled by the activities of sialyltranferases and sialidases. To address the impact of sialidase (neu1) activity on lipoprotein metabolism, we have generated a mouse model with a hypomorphic neu1 allele (B6.SM) that displays reduced sialidase expression and sialidase activity. The objectives of this study are to determine the impact of sialidase on the rate of hepatic lipoprotein secretion and lipoprotein uptake. Our results indicate that hepatic levels of cholesterol and triglycerides are significantly higher in B6.SM mice compared with C57Bl/6 mice; however, VLDL-triglyceride production rate is lower. In addition, B6.SM mice show significantly lower levels of hepatic microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) and active sterol-regulatory element binding protein (SREBP)-2 but higher levels of diglyceride acyltransferase (DGAT)2; these are all indicative of increased hepatic lipid storage. Rescue of sialidase activity in hypomorphic sialidase mice using helper-dependent adenovirus resulted in increased VLDL production and an increase in MTP levels. Furthermore, hypomorphic sialidase expression results in stabilization of hepatic LDL receptor (LDLR) protein expression, which enhances LDL uptake. These findings provide novel evidence for a central role of sialidase in the cross talk between the uptake and production of lipoproteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sialidase down-regulation reduces non-HDL cholesterol, inhibits leukocyte transmigration, and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 21;293(38):14689-14706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004589. Epub 2018 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30097518 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenger receptor BI facilitates hepatic very low density lipoprotein production in mice.J Lipid Res. 2010 Mar;51(3):544-53. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M000844. Epub 2009 Sep 1. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19723664 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted deletion of hepatocyte ABCA1 leads to very low density lipoprotein triglyceride overproduction and low density lipoprotein hypercatabolism.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 16;285(16):12197-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.096933. Epub 2010 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20178985 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and hepatic lipoprotein assembly and secretion.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000 Dec 15;1529(1-3):223-30. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(00)00151-7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000. PMID: 11111091 Review.
-
Recent advances in physiological lipoprotein metabolism.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014 Dec;52(12):1695-727. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2013-0358. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014. PMID: 23940067 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuraminidase1 Inhibitor Protects Against Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Suppressing Drp1-Dependent Mitophagy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 17;9:802502. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.802502. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34977042 Free PMC article.
-
ASGR1 - a new target for lowering non-HDL cholesterol.Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2016 Jun 30;2016(2):e201614. doi: 10.21542/gcsp.2016.14. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2016. PMID: 29043262 Free PMC article.
-
Neuraminidases-Key Players in the Inflammatory Response after Pathophysiological Cardiac Stress and Potential New Therapeutic Targets in Cardiac Disease.Biology (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;11(8):1229. doi: 10.3390/biology11081229. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Atherogenic Role of Circulating Modified Lipids in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 20;20(14):3561. doi: 10.3390/ijms20143561. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31330845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialidase down-regulation reduces non-HDL cholesterol, inhibits leukocyte transmigration, and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE knockout mice.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 21;293(38):14689-14706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004589. Epub 2018 Aug 10. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30097518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hegele R. A. 2009. Plasma lipoproteins: genetic influences and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10: 109–121 - PubMed
-
- Glass C. K., Witztum J. L. 2001. Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell. 104: 503–516 - PubMed
-
- Reuter G., Gabius H. J. 1996. Sialic acids structure-analysis-metabolism-occurrence-recognition. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler. 377: 325–342 - PubMed
-
- Collard J. G., Schijven J. F., Bikker A., La R. G., Bolscher J. G., Roos E. 1986. Cell surface sialic acid and the invasive and metastatic potential of T-cell hybridomas. Cancer Res. 46: 3521–3527 - PubMed
-
- Pilatte Y., Bignon J., Lambre C. R. 1993. Sialic acids as important molecules in the regulation of the immune system: pathophysiological implications of sialidases in immunity. Glycobiology. 3: 201–218 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

