14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ inhibit Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated proinflammatory cytokine induction
- PMID: 22984265
- PMCID: PMC3493911
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.367490
14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ inhibit Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated proinflammatory cytokine induction
Retraction in
-
14-3-3ϵ and 14-3-3σ inhibit Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated proinflammatory cytokine induction.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 12;289(37):25474. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A112.367490. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25217707 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
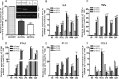
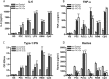
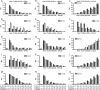
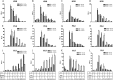
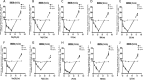
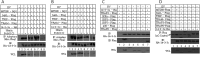
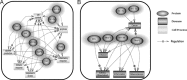
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a group of pattern recognition receptors that play a crucial role in the induction of the innate immune response against bacterial and viral infections. TLR3 has emerged as a key sensor of viral double-stranded RNA. Thus, a clearer understanding of the biological processes that modulate TLR3 signaling is essential. Limited studies have applied proteomics toward understanding the dynamics of TLR signaling. Herein, a proteomics approach identified 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ proteins as new members of the TLR signaling complex. Toward the functional characterization of 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ in TLR signaling, we have shown that both of these proteins impair TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR7/8, and TLR9 ligand-induced IL-6, TNFα, and IFN-β production. We also show that 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ impair TLR2-, TLR3-, TLR4-, TLR7/8-, and TLR9-mediated NF-κB and IFN-β reporter gene activity. Interestingly, although the 14-3-3 proteins inhibit poly(I:C)-mediated RANTES production, 14-3-3 proteins augment Pam(3)CSK(4), LPS, R848, and CpG-mediated production of RANTES (regulated on activation normal T cell expressed and secreted) in a Mal (MyD88 adaptor-like)/MyD88-dependent manner. 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ also bind to the TLR adaptors and to both TRAF3 and TRAF6. Our study conclusively shows that 14-3-3ε and 14-3-3σ play a major regulatory role in balancing the host inflammatory response to viral and bacterial infections through modulation of the TLR signaling pathway. Thus, manipulation of 14-3-3 proteins may represent novel therapeutic targets for inflammatory conditions and infections.
Figures


References
-
- Miggin S. M., O'Neill L. A. (2006) New insights into the regulation of TLR signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 80, 220–226 - PubMed
-
- Keating S. E., Baran M., Bowie A. G. (2011) Cytosolic DNA sensors regulating type I interferon induction. Trends Immunol. 32, 574–581 - PubMed
-
- Kumar H., Kawai T., Akira S. (2009) Pathogen recognition in the innate immune response. Biochem. J. 420, 1–16 - PubMed
-
- O'Neill L. A., Bowie A. G. (2007) The family of five. TIR domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat. Rev. 7, 353–364 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

