Apoptosis induced by knockdown of uPAR and MMP-9 is mediated by inactivation of EGFR/STAT3 signaling in medulloblastoma
- PMID: 22984561
- PMCID: PMC3440337
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044798
Apoptosis induced by knockdown of uPAR and MMP-9 is mediated by inactivation of EGFR/STAT3 signaling in medulloblastoma
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Apoptosis Induced by Knockdown of uPAR and MMP-9 is Mediated by Inactivation of EGFR/STAT3 Signaling in Medulloblastoma.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 15;20(7):e0328377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328377. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40663504 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Medulloblastoma is a highly invasive cancer of central nervous system diagnosed mainly in children. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) are over expressed in several cancers and well established for their roles in tumor progression. The present study is aimed to determine the consequences of targeting these molecules on medulloblastoma progression.
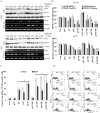
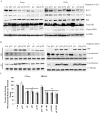
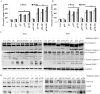
Methodology/principal findings: Radiation is one of the foremost methods applied for treating cancer and considerable evidence showed that radiation elevated uPAR and MMP-9 expression in medulloblastoma cell. Therefore efforts are made to target these molecules in non-irradiated and irradiated medulloblastoma cells. Our results showed that siRNA-mediated knockdown of uPAR and MMP-9, either alone or in combination with radiation modulated a series of events leading to apoptosis. Down regulation of uPAR and MMP-9 inhibited the expression of anti-apoptotic molecules like Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, survivin, XIAP and cIAPI; activated BID cleavage, enhanced the expression of Bak and translocated cyctochrome C to cytosol. Capsase-3 and -9 activities were also increased in uPAR- and MMP-9-downregulated cells. The apoptosis induced by targeting MMP-9 and uPAR was initiated by inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mediated activation of STAT3 and NF-κB related signaling molecules. Silencing uPAR and MMP-9 inhibited DNA binding activity of STAT3 and also reduced the recruitment of STAT3 protein at the promoter region of Bcl-2 and survivin genes. Our results suggest that inhibiting uPAR and MMP-9 reduced the expression of anti-apoptotic molecules by inactivating the transcriptional activity of STAT3. In addition, treating pre-established medulloblastoma with siRNAs against uPAR and MMP-9 both alone or in combination with radiation suppressed uPAR, MMP-9, EGFR, STAT3 expression and induced Bak activation leading to apoptosis.
Conclusion/significance: Taken together, our results illustrated that RNAi mediated targeting of uPAR and MMP-9 might have therapeutic potential against medulloblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Rood BR, MacDonald TJ, Packer RJ (2004) Current treatment of medulloblastoma: recent advances and future challenges. Semin Oncol 31: 666–675. - PubMed
-
- Crawford JR, MacDonald TJ, Packer RJ (2007) Medulloblastoma in childhood: new biological advances. Lancet Neurol 6: 1073–1085. - PubMed
-
- Rao JS (2003) Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 489–501. - PubMed
-
- Murphy G, Docherty AJ (1992) The matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 7: 120–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

