Myelin-derived lipids modulate macrophage activity by liver X receptor activation
- PMID: 22984598
- PMCID: PMC3440367
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044998
Myelin-derived lipids modulate macrophage activity by liver X receptor activation
Abstract
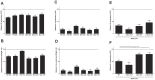
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic, inflammatory, demyelinating disease of the central nervous system in which macrophages and microglia play a central role. Foamy macrophages and microglia, containing degenerated myelin, are abundantly found in active multiple sclerosis lesions. Recent studies have described an altered macrophage phenotype after myelin internalization. However, it is unclear by which mechanisms myelin affects the phenotype of macrophages and how this phenotype can influence lesion progression. Here we demonstrate, by using genome wide gene expression analysis, that myelin-phagocytosing macrophages have an enhanced expression of genes involved in migration, phagocytosis and inflammation. Interestingly, myelin internalization also induced the expression of genes involved in liver-X-receptor signaling and cholesterol efflux. In vitro validation shows that myelin-phagocytosing macrophages indeed have an increased capacity to dispose intracellular cholesterol. In addition, myelin suppresses the secretion of the pro-inflammatory mediator IL-6 by macrophages, which was mediated by activation of liver-X-receptor β. Our data show that myelin modulates the phenotype of macrophages by nuclear receptor activation, which may subsequently affect lesion progression in demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Brosnan CF, Bornstein MB, Bloom BR (1981) The effects of macrophage depletion on the clinical and pathologic expression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 126: 614–620. - PubMed
-
- Hellings N, Raus J, Stinissen P (2002) Insights into the immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Immunol Res 25: 27–51. - PubMed
-
- Vanderlocht J, Hellings N, Hendriks JJ, Stinissen P (2007) The ambivalent nature of T-cell infiltration in the central nervous system of patients with multiple sclerosis. Crit Rev Immunol 27: 1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

