Trends in overweight and obesity in Lebanon: evidence from two national cross-sectional surveys (1997 and 2009)
- PMID: 22984791
- PMCID: PMC3527186
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-798
Trends in overweight and obesity in Lebanon: evidence from two national cross-sectional surveys (1997 and 2009)
Abstract
Background: Even though the obesity epidemic continues to grow in various parts of the world, recent reports have highlighted disparities in obesity trends across countries. There is little empirical evidence on the development and growth of obesity in Lebanon and other countries of the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Acknowledging the need for effective obesity preventive measures and for accurate assessment of trends in the obesity epidemic, this study aims at examining and analyzing secular trends in the prevalence of overweight and obesity over a 12-year period in Lebanon.
Methods: Based on weight and height measurements obtained from two national cross-sectional surveys conducted in 1997 and 2009 on subjects 6 years of age and older, BMI was calculated and the prevalence of obesity was determined based on BMI for adults and BMI z-scores for children and adolescents, according to WHO criteria. Age -and sex- adjusted odds ratios for overweight and obesity were determined, with the 1997 year as the referent category. Annual rates of change in obesity prevalence per sex and age group were also calculated.
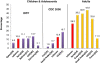
Results: The study samples included a total of 2004 subjects in the 1997 survey and 3636 in the 2009 survey. Compared to 1997, mean BMI values were significantly higher in 2009 among all age and sex groups, except for 6-9 year old children. Whereas the prevalence of overweight appeared stable over the study period in both 6-19 year old subjects (20.0% vs. 21.2%) and adults aged 20 years and above (37.0% vs. 36.8%), the prevalence of obesity increased significantly (7.3% vs. 10.9% in 6-19 year olds; 17.4% vs. 28.2% in adults), with the odds of obesity being 2 times higher in 2009 compared to 1997, in both age groups (OR = 1.96, 95% CI:1.29-2.97 and OR = 2.01, 95% CI: 1.67-2.43, respectively). The annual rates of change in obesity prevalence ranged between +4.1% in children and adolescents and +5.2% in adults.
Conclusion: The study's findings highlight an alarming increase in obesity prevalence in the Lebanese population, over the 12-year study period, and alert to the importance of formulating policies and nutritional strategies to curb the obesity rise in the country.
Figures
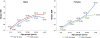
References
-
- Ng SW, Zaghloul S, Ali HI, Harrison G, Popkin BM. The prevalence and trends of overweight, obesity and nutrition-related non-communicable diseases in the Arabian Gulf States. Obes Rev. 2011;12:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, Farzadfar F, Riley LM, Ezzati M. on behalf of the Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Body Mass Index) National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:557–567. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

