SR-BI associates with ABCG1 and inhibits ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux from cells to high-density lipoprotein 3
- PMID: 22984960
- PMCID: PMC3512508
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-118
SR-BI associates with ABCG1 and inhibits ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux from cells to high-density lipoprotein 3
Abstract
Background: The single and combined effects of scavenger receptor-BI (SR-BI), ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) A1 and G1 on cholesterol efflux from Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells were investigated.
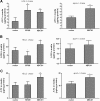
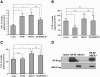
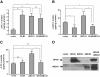
Results: When apolipoproteinA-I (apoA-I) was used as an acceptor, ABCA1 overexpression led to an increase in total cholesterol (TC) in medium which is attributable to a 2-fold increase in free cholesterol (FC) content. When high-density lipoprotein 3 (HDL3) was used as an acceptor, SR-BI overexpression not only promoted FC efflux, but also promoted the uptake of cholesteryl ester (CE) into cells, resulting in no TC varieties in medium. Overexpression of ABCG1 increased both the FC and CE levels in medium. However, when apoA-I and HDL3 were both used as acceptors, coexpression of SR-BI has no effect on ABCA1-mediated increased FC and TC accumulation in medium. Interestingly, coexpression of SR-BI with ABCG1 blocked the ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux to HDL3, mostly by promoting the reuptake of CE from the medium. Furthermore, co-immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that SR-BI interacted with ABCG1 in BHK cells overexpressing ABCG1 and SR-BI.
Conclusions: We found SR-BI associates with ABCG1 and inhibits ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux from cells to HDL3.
Figures
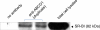
Similar articles
-
Adipocyte modulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Circulation. 2010 Mar 23;121(11):1347-55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.897330. Epub 2010 Mar 8. Circulation. 2010. PMID: 20212278 Free PMC article.
-
SR-BI inhibits ABCG1-stimulated net cholesterol efflux from cells to plasma HDL.J Lipid Res. 2008 Jan;49(1):107-14. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700200-JLR200. Epub 2007 Oct 24. J Lipid Res. 2008. PMID: 17960026
-
13-hydroxy linoleic acid increases expression of the cholesterol transporters ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-BI and stimulates apoA-I-dependent cholesterol efflux in RAW264.7 macrophages.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 Nov 30;10:222. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-222. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 22129452 Free PMC article.
-
Foam cells in atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:245-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23782937 Review.
-
Different Pathways of Cellular Cholesterol Efflux.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2022 Sep;80(3):471-481. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01081-5. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35737216 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of Blood Lipoprotein and Lipid Fraction Profiles in Healthy Subjects through Integrated Univariate, Multivariate, and Network Analysis Reveals Association of Lipase Activity and Cholesterol Esterification with Sex and Age.Metabolites. 2021 May 18;11(5):326. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050326. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34070169 Free PMC article.
-
The Ratio of Unesterified/esterified Cholesterol is the Major Determinant of Atherogenicity of Lipoprotein Fractions.Med Arch. 2018 Apr;72(2):103-107. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2018.72.103-107. Med Arch. 2018. PMID: 29736097 Free PMC article.
-
Danshensu Promotes Cholesterol Efflux in RAW264.7 Macrophages.Lipids. 2016 Sep;51(9):1083-92. doi: 10.1007/s11745-016-4178-1. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Lipids. 2016. PMID: 27514857
-
Nintedanib ameliorates oxidized low-density lipoprotein -induced inflammation and cellular senescence in vascular endothelial cells.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):6196-6207. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2036913. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35236245 Free PMC article.
-
Brown Algae Potential as a Functional Food against Hypercholesterolemia: Review.Foods. 2021 Jan 24;10(2):234. doi: 10.3390/foods10020234. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33498824 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tall AR. An overview of reverse cholesterol transport. Eur Heart J. 1998;19(Suppl A):A31–A35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

