Pathogen recognition in the human female reproductive tract: expression of intracellular cytosolic sensors NOD1, NOD2, RIG-1, and MDA5 and response to HIV-1 and Neisseria gonorrhea
- PMID: 22984986
- PMCID: PMC3518676
- DOI: 10.1111/aji.12019
Pathogen recognition in the human female reproductive tract: expression of intracellular cytosolic sensors NOD1, NOD2, RIG-1, and MDA5 and response to HIV-1 and Neisseria gonorrhea
Abstract
Problem: Expression patterns and regulation of cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRR) NOD-1, NOD-2, RIG-1, and MDA5 have not been elucidated in the human female reproductive tract (FRT).
Method of study: Primary epithelial cells (EC) isolated from Fallopian tube (FT), endometrium (EM), cervix (Cx), and ectocervix (Ecx) were treated with estradiol, poly(I:C), Neisseria gonorrhea (GC), and HIV-1. PRR mRNA expressions were analyzed by Real-time RT-PCR. Conditioned media were analyzed for IL-8 by ELISA.
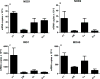
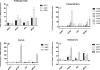
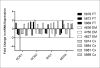
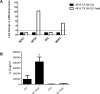
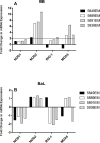
Results: EC from all FRT compartments constitutively expressed NOD1, NOD2, RIG-1, and MDA5 with highest levels expressed by FT. Stimulation with poly(I:C) resulted in upregulation of NOD2, RIG-1, and MDA5 in all FRT compartments and correlated with increased secretion of IL-8, whereas estradiol treatment had no effects. Exposure to GC and HIV-1 IIIB but not BaL resulted in selective upregulation of NOD2 and MDA5.
Conclusion: PRR are expressed throughout the FRT and differentially regulated by poly(I:C), GC and HIV-1.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NOD-like receptors and RIG-I-like receptors in human eosinophils: activation by NOD1 and NOD2 agonists.Immunology. 2011 Nov;134(3):314-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03492.x. Immunology. 2011. PMID: 21978001 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NOD receptors by Neisseria gonorrhoeae modulates the innate immune response.Innate Immun. 2014 May;20(4):377-89. doi: 10.1177/1753425913493453. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Innate Immun. 2014. PMID: 23884094 Free PMC article.
-
Functional expression of pattern recognition receptors in tissues of the human female reproductive tract.J Reprod Immunol. 2009 Jun;80(1-2):33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2008.12.004. Epub 2009 Apr 29. J Reprod Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19406482 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the inflammasome: regulatory NOD-like receptor modulation of the host immune response following virus exposure.J Gen Virol. 2016 Apr;97(4):825-838. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000401. Epub 2016 Jan 13. J Gen Virol. 2016. PMID: 26763980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of sex hormones and the tissue environment in immune protection against HIV in the female reproductive tract.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014 Aug;72(2):171-81. doi: 10.1111/aji.12235. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24661500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of sex hormones in immune protection of the female reproductive tract.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Apr;15(4):217-30. doi: 10.1038/nri3819. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25743222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Transcriptional Response in Head Kidney Primary Cell Cultures Isolated from the Three Most Important Species in Chilean Salmonids Aquaculture.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;12(7):924. doi: 10.3390/biology12070924. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508355 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of RIP1 and IPS-1 in chronic HBV infected patients.Genet Mol Biol. 2019 Apr-Jun;42(2):337-343. doi: 10.1590/1678-4685-GMB-2018-0071. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Genet Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31429854 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and the Host Defense in Ascending Infections of Human Fallopian Tube.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 21;9:2710. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02710. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30524442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between sex hormones, the vaginal microbiome and immunity in HIV-1 susceptibility in women.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Aug 28;11(9):dmm035147. doi: 10.1242/dmm.035147. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 30154116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wira CR, Fahey JV, Ghosh M, Patel MV, Hickey DK, Ochiel DO. Sex hormone regulation of innate immunity in the female reproductive tract: the role of epithelial cells in balancing reproductive potential with protection against sexually transmitted pathogens. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010;63:544–565. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kopp EB, Medzhitov R. The Toll-receptor family and control of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999;11:13–18. - PubMed
-
- Inohara N, Nunez G. NODs: intracellular proteins involved in inflammation and apoptosis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:371–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

