Sustainable prevention of obesity through integrated strategies: The SPOTLIGHT project's conceptual framework and design
- PMID: 22985293
- PMCID: PMC3490949
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-793
Sustainable prevention of obesity through integrated strategies: The SPOTLIGHT project's conceptual framework and design
Abstract
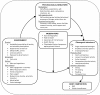
Background: The prevalence of overweight and obesity in Europe is high. It is a major cause of the overall rates of many of the main chronic (or non communicable) diseases in this region and is characterized by an unequal socio-economic distribution within the population. Obesity is largely determined by modifiable lifestyle behaviours such as low physical activity levels, sedentary behaviour and consumption of energy dense diets. It is increasingly being recognised that effective responses must go beyond interventions that only focus on a specific individual, social or environmental level and instead embrace system-based multi-level intervention approaches that address both the individual and environment. The EU-funded project "sustainable prevention of obesity through integrated strategies" (SPOTLIGHT) aims to increase and combine knowledge on the wide range of determinants of obesity in a systematic way, and to identify multi-level intervention approaches that are strong in terms of Reach, Efficacy, Adoption, Implementation and Maintenance (RE-AIM).
Methods/design: SPOTLIGHT comprises a series of systematic reviews on: individual-level predictors of success in behaviour change obesity interventions; social and physical environmental determinants of obesity; and on the RE-AIM of multi-level interventions. An interactive web-atlas of currently running multi-level interventions will be developed, and enhancing and impeding factors for implementation will be described. At the neighbourhood level, these elements will inform the development of methods to assess obesogenicity of diverse environments, using remote imaging techniques linked to geographic information systems. The validity of these methods will be evaluated using data from surveys of health and lifestyles of adults residing in the neighbourhoods surveyed. At both the micro- and macro-levels (national and international) the different physical, economical, political and socio-cultural elements will be assessed.
Discussion: SPOTLIGHT offers the potential to develop approaches that combine an understanding of the obesogenicity of environments in Europe, and thus how they can be improved, with an appreciation of the individual factors that explain why people respond differently to such environments. Its findings will inform governmental authorities and professionals, academics, NGOs and private sector stakeholders engaged in the development and implementation of policies to tackle the obesity epidemic in Europe.
Figures
References
-
- OECD. Obesity update 2012. 2012. www.oecd.org/dataoecd/1/61/49716427.pdf.
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. WHO fact sheet 2012, N°311. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical