Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibition with simvastatin in acute lung injury to reduce pulmonary dysfunction (HARP-2) trial: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 22985805
- PMCID: PMC3543316
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-13-170
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibition with simvastatin in acute lung injury to reduce pulmonary dysfunction (HARP-2) trial: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) is a common devastating clinical syndrome characterized by life-threatening respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation and multiple organ failure. There are in vitro, animal studies and pre-clinical data suggesting that statins may be beneficial in ALI. The Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibition with simvastatin in Acute lung injury to Reduce Pulmonary dysfunction (HARP-2) trial is a multicenter, prospective, randomized, allocation concealed, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial which aims to test the hypothesis that treatment with simvastatin will improve clinical outcomes in patients with ALI.
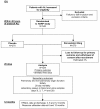
Methods/design: Patients fulfilling the American-European Consensus Conference Definition of ALI will be randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive enteral simvastatin 80 mg or placebo once daily for a maximum of 28 days. Allocation to randomized groups will be stratified with respect to hospital of recruitment and vasopressor requirement. Data will be recorded by participating ICUs until hospital discharge, and surviving patients will be followed up by post at 3, 6 and 12 months post randomization. The primary outcome is number of ventilator-free days to day 28. Secondary outcomes are: change in oxygenation index and sequential organ failure assessment score up to day 28, number of non pulmonary organ failure free days to day 28, critical care unit mortality; hospital mortality; 28 day post randomization mortality and 12 month post randomization mortality; health related quality of life at discharge, 3, 6 and 12 months post randomization; length of critical care unit and hospital stay; health service use up to 12 months post-randomization; and safety. A total of 540 patients will be recruited from approximately 35 ICUs in the UK and Ireland. An economic evaluation will be conducted alongside the trial. Plasma and urine samples will be taken up to day 28 to investigate potential mechanisms by which simvastatin might act to improve clinical outcomes.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN88244364.
References
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149:818–824. - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Minelli C, Bertolini G, Brazzi L, Pimentel J, Lewandowski K, Bion J, Romand JA, Villar J, Thorsteinsson A, Damas P, Armaganidis A, Lemaire F. ALIVE Study Group. Epidemiology and outcome of acute lung injury in European intensive care units. Results from the ALIVE study. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:51–61. doi: 10.1007/s00134-003-2022-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical