Reversal of inhibition of putative dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area: interaction of GABA(B) and D2 receptors
- PMID: 22986166
- PMCID: PMC3490029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.08.045
Reversal of inhibition of putative dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area: interaction of GABA(B) and D2 receptors
Abstract
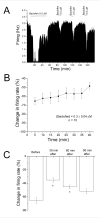
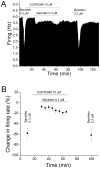
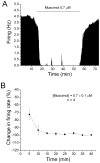
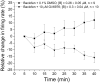
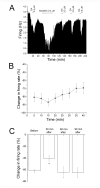
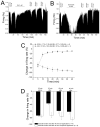
Neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA) are critical in the rewarding and reinforcing properties of drugs of abuse. Desensitization of VTA neurons to moderate extracellular concentrations of dopamine (DA) is dependent on protein kinase C (PKC) and intracellular calcium levels. This desensitization is called DA inhibition reversal, as it requires concurrent activation of D2 and D1-like receptors; activation of D2 receptors alone does not result in desensitization. Activation of other G-protein-linked receptors can substitute for D1 activation. Like D2 receptors, GABA(B) receptors in the VTA are coupled to G-protein-linked potassium channels. In the present study, we examined interactions between a GABA(B) agonist, baclofen, and dopamine agonists, dopamine and quinpirole, to determine whether there was some interaction in the processes of desensitization of GABA(B) and D2 responses. Long-duration administration of baclofen alone produced reversal of the baclofen-induced inhibition indicative of desensitization, and this desensitization persisted for at least 60 min after baclofen washout. Desensitization to baclofen was dependent on PKC. Dopamine inhibition was reduced for 30 min after baclofen-induced desensitization and conversely, the magnitude of baclofen inhibition was reduced for 30 min by long-duration application of dopamine, but not quinpirole. These results indicate that D2 and GABA(B) receptors share some PKC-dependent mechanisms of receptor desensitization.
Copyright © 2012 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: None of the authors have any conflict of interest associated with the content of this report.
Figures
References
-
- Ackerman JM, Johansen PA, Clark D, White FJ. Electrophysiological effects of putative autoreceptor-selective dopamine agonists on A10 dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:963–970. - PubMed
-
- Arora D, Hearing M, Haluk DM, Mirkovic K, Fajardo-Serrano A, Wessendorf MW, Watanabe M, Lujan R, Wickman K. Acute cocaine exposure weakens GABA(B) receptor-dependent G-protein-gated inwardly rectifying K+ signaling in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci. 2011;31:12251–12257. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bofill-Cardona E, Kudlacek O, Yang Q, Ahorn H, Freissmuth M, Nanoff C. Binding of calmodulin to the D2-dopamine receptor reduces receptor signaling by arresting the G protein activation switch. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:32672–32680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

